Figure 1.
Mutant screen for PIN3 polarization defects in hypocotyl gravitropism.
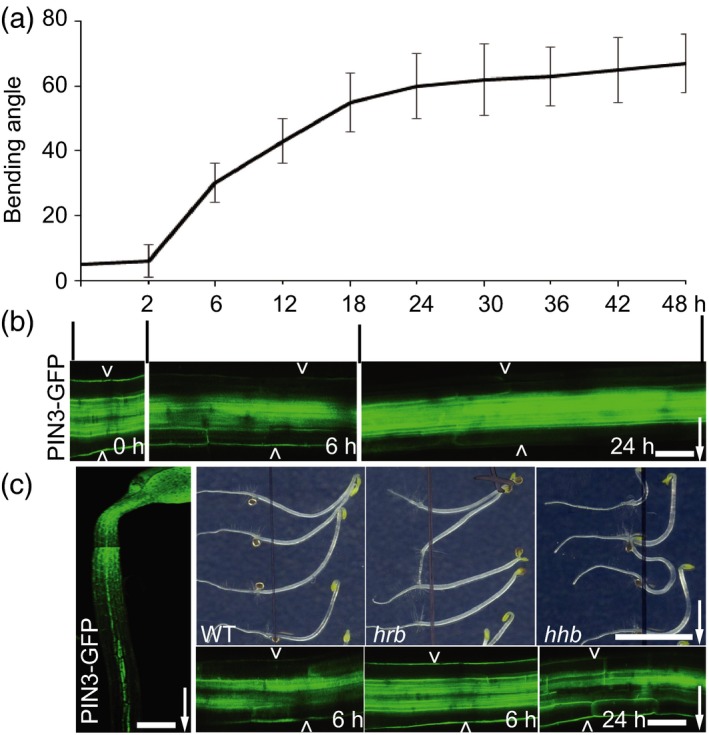
(a) Arabidopsis hypocotyl bending kinetics. Three‐day‐old etiolated seedlings were gravistimulated and bending angle was measured at indicated time intervals (h), data referred from Rakusová et al. (2016); N > 20 seedlings.
(b) PIN3‐GFP polarization at different stages of gravitropic response. Before gravity stimulation, PIN3‐GFP is symmetric at both sides of endodermal cells. Starting at 2 h, PIN3‐GFP is enriched at the lower side of endodermal cells. After approximately 18 h, PIN3‐GFP at the lower hypocotyl side starts to disappear from the outer sides of endodermal cells restoring the symmetry between the upper and lower sides of the hypocotyl. Pictures were taken at 0, 6 and 24 h after gravity stimulation. Scale bar: 20 μm. Arrow indicates gravity direction.
(c) Design of the forward genetic screen for novel PIN3 polarity regulators. Ethyl methylsulfonate (EMS)‐mutagenized 3‐day‐old etiolated PIN3::PIN3‐GFP seedlings were gravity stimulated for 6 or 24 h. Seedlings with reduced bending (hrb mutants) or hyperbending (hhb mutants) response were selected as candidates. PIN3‐GFP relocation after gravity stimulation was analyzed in selected mutants. Typically, in the hrb mutants PIN3‐GFP did not show a relocation after 6 h gravistimulation, while hhb mutants showed PIN3‐GFP persisting at the outer sides of endodermal cells at the bottom hypocotyl side even at later time points (24 h). Scale bar: 60 μm (left‐side image) and 20 μm (gravity stimulated PIN3::PIN3‐GFP), and 2 cm for phenotype images. Arrowheads depict outer sides of endodermal cells. Arrow indicates gravity direction.
