Figure 1.
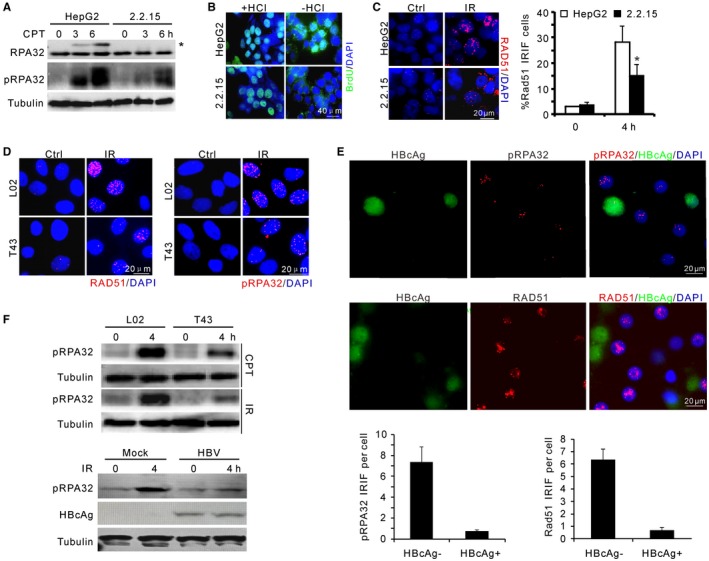
HBV attenuates DNA end resection upon genotoxic insults. (A) Immunoblotting for RPA32 phosphorylation in HepG2 and HepG2.2.15 cells upon CPT treatment. pRPA32 indicates phosphorylated serine 33 of RPA32. *Band shift of phosphorylated RPA32 detected by α‐RPA32 serum. (B) Non‐(−HCl) and denaturing‐(+HCl) indirect immunofluorescence showing ssDNA at resected DSBs and equal incorporation of BrdU after CPT treatment, respectively. Scale bar, 40 μm. (C) Representative image and percentage of RAD51 IRIF‐positive cells after 5‐Gy irradiation in HepG2 and HepG2.2.15 cells. (D) Representative images for IRIF of RAD51 and phosphorylated RPA32 in L02 and T43 cells after IR treatment. (E) Images (top) and quantification (bottom) of indicated IRIF in mock or HBV‐infected PHHs at day 7. Cells were fixed for immunostaining 4 hours after 1‐Gy irradiation. HBcAg (green) marks HBV‐infected PHHs. (F) Immunoblotting for RPA32 phosphorylation in L02/T43 cells or HBV‐infected PHHs at indicated times. Genotoxic treatments: 2 μM CPT or 5‐Gy irradiation. Abbreviation: DAPI, 4′,6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole.
