Figure 6:
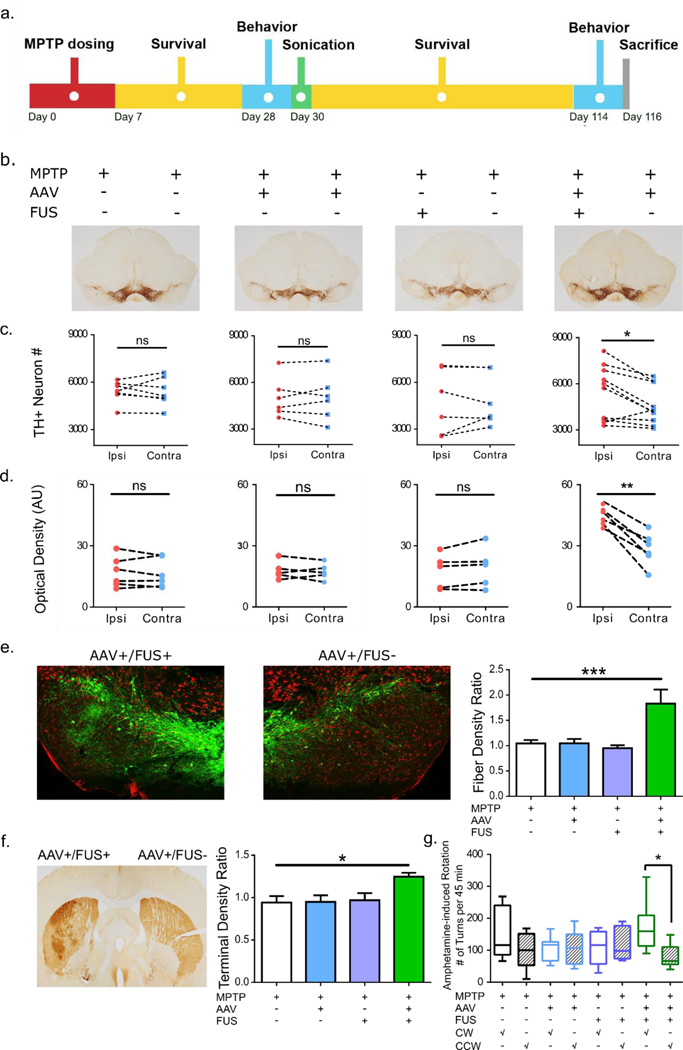
FUS-facilitated AAV-GDNF delivery induced neuronal upregulation in MPTP mice. a. Experimental timeline where MPTP was given first followed by sonication and a 12-week survival period. Behavioral studies were performed 1 week prior to sonication and repeated at the end of the survival period. b. TH staining of the SN region in mice receiving a combination of AAV/FUS treatments (n=6–10). c. TH+ neurons were counted and intra-group comparisons were made. Significantly higher number of TH+ neurons were found on the AAV+/FUS+ side of the brain compared to the contralateral side. d. TH+ dendrite density was calculated and intra-group comparisons were performed. Significantly higher dendrite density was observed on the AAV+/FUS+ side of the brain. e. Immunofluorescent TH staining revealed much more dopaminergic projections on the AAV+/FUS+ side of the brain. Dendritic densities of the SN region were compared across groups and significantly higher dendritic fiber network (n=4–5; F[3, 13] = 7.514; P=0.0036) was identified comparing AAV+/FUS+ to the MPTP group. f. TH staining of the striatum illustrates the ameliorated dopaminergic projections on the AAV+/FUS+ hemisphere. Quantitative analysis of the optical density ratio demonstrated significant difference (n=4–5; F[3, 17] = 4.733; P=0.014) between the AAV+/FUS+ to the MPTP group. g. Amphetamine-elicited behavioral studies revealed more frequent clockwise (toward the remaining lesion side) rotation, signifying more prominent dopaminergic function on the hemisphere receiving AAV+/FUS+ treatment.
