Figure 6.
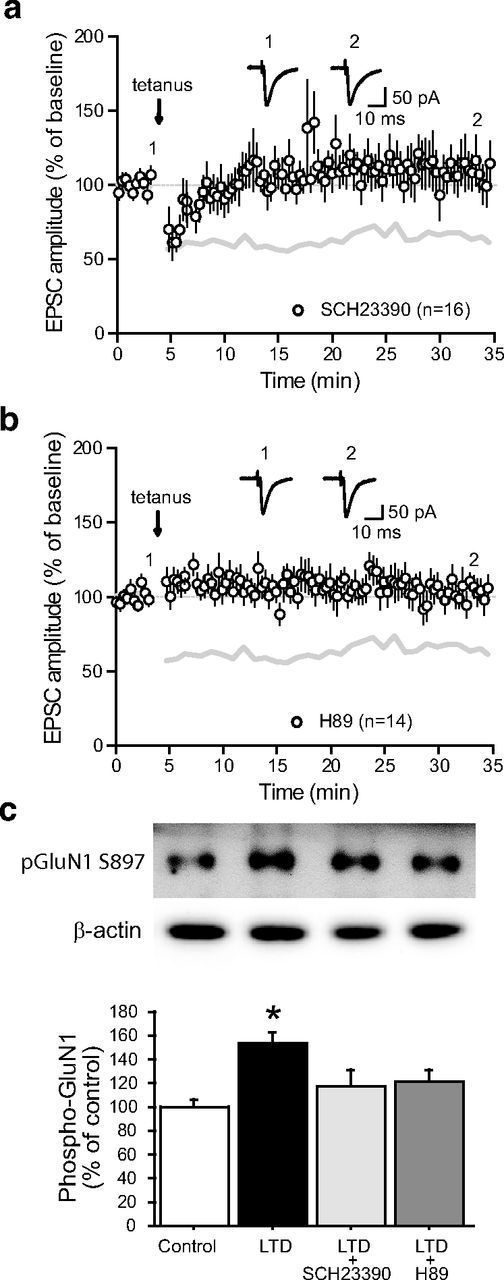
Acute dopaminergic modulation of subthalamo-nigral LTD. a, LTD induction protocol in the presence of the D1/5 receptor antagonist SCH23390 (5 μm; n = 16). Inset, Traces from a representative experiment illustrating the average eEPSC from 0 to 5 min (1) and 30 to 35 min (2). The gray lines in a and b represent the shape of control tetanus-induced LTD from Figure 2a for comparison (control vs SCH23390, p < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test). b, LTD induction protocol in the presence of the PKA antagonist H89 (10 μm; n = 14; control vs H89, p < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test). Inset, Traces from a representative experiment illustrating the average eEPSC from 0 to 5 min (1) and 30 to 35 min (2). c, D1/5 receptors and PKA are specifically involved in the phosphorylation of the NMDA receptor GluN1 subunit during LTD induction. The levels of phospho[Ser-897]-GluN1 were determined as described in Materials and Methods. Top, Representative autoradiograms. Bottom, Summary of data expressed as means ± SEM (n = 3). The amount of phosphorylated GluN1 is expressed as a percentage of that determined in basal condition (control). The increased phosphorylation of GluN1 triggered by LTD induction was prevented by the D1/5 receptor antagonist SCH23390 (10 μm) and the PKA inhibitor H89 (10 μm). *p = 0.007 versus respective control group; one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test.
