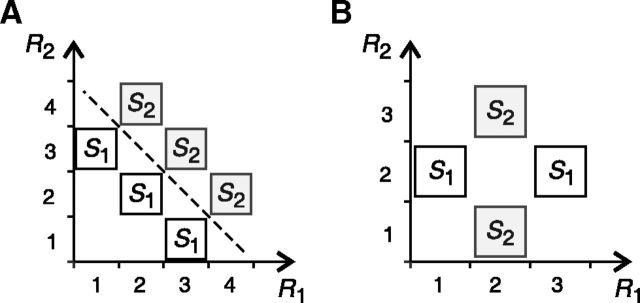
Figure 2.
Comparison of different strategies to construct decoders that ignore noise correlations. Each panel shows the simultaneous responses of two neurons R1 and R2 elicited by two stimuli S1 and S2. In both examples, stimuli and responses are equally likely. A, Linear decoders trained with surrogate NI population responses (dashed line) extract all the encoded information, whereas no probabilistic NI decoder can do so. Specifically, a probabilistic NI decoder is inefficient for a range of probabilities P(R1,R2|Sk) complying with the two following conditions: P(2,2|S1)2 = P(1,3|S1) P(3,1|S1) and P(3, 3|S2)2 = P(2,4|S2) P(4,2|S2). B, Although neurons are noise independent, no linear decoder is capable of extracting all of the encoded information.