Figure 8.
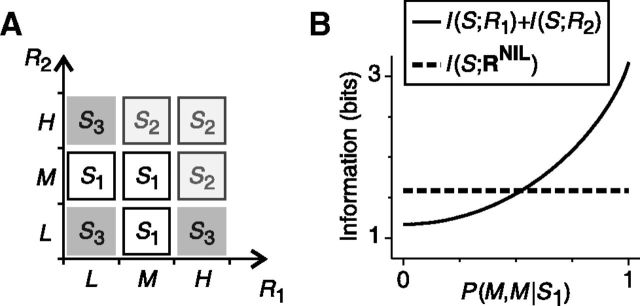
The NI decoder can paradoxically extract more information than that encoded by individual neurons. A, Example showing the responses of two neurons R1 and R2 elicited by three stimuli S1, S2, and S3. All stimuli are equally likely. Response probabilities P(L,L|S3), P(M,M|S1), and P(H,H|S2) are equal to α and response probabilities P(L,M|S1), P(M,L|S1), P(L,H|S3), P(H,L|S3), P(M,H|S2), and P(H,M|S2) are equal to 0.5 − α/2, with α varying between 0 and 1. B, The NI decoder is capable of extracting more information than the sum of the information encoded by individual neurons for a wide range of response probabilities. This effect is enhanced by the fact that the latter information is only an upper bound of the information conveyed individually by the neurons in the population.