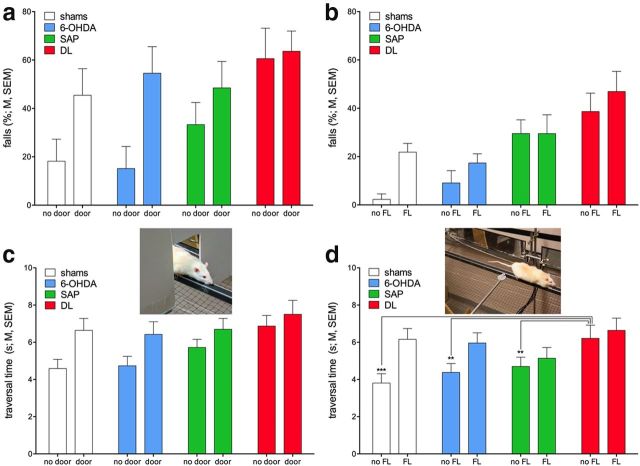
Figure 6.
DL rats again generally fell more frequently than all other rats, and the door frame (a) as well as the FL (b) distractor increased falls in all rats (see Results for main effects; N = 44, n = 11 per group). As we hypothesized that the distractors were less effectively processed in rats with loss of cholinergic neurons (SAP and DL), we also analyzed traversal time in trials in which the distractors did not produce falls and, in case of the FL distractor, did not generate retrieval attempts (c,d). Traversal speed slowed in the presence of distractors in shams and 6-OHDA rats, yielding a significant interaction between distactor and group in the analysis of the effects of the DL distractor. d, Results of post hoc one-way ANOVAs indicating that shams, 6-OHDA, and SAP rats were faster than DL rats in the absence of the distractor but that distractor-induced slowing of the traversal speed of shams and 6-OHDA rats abolished this difference.