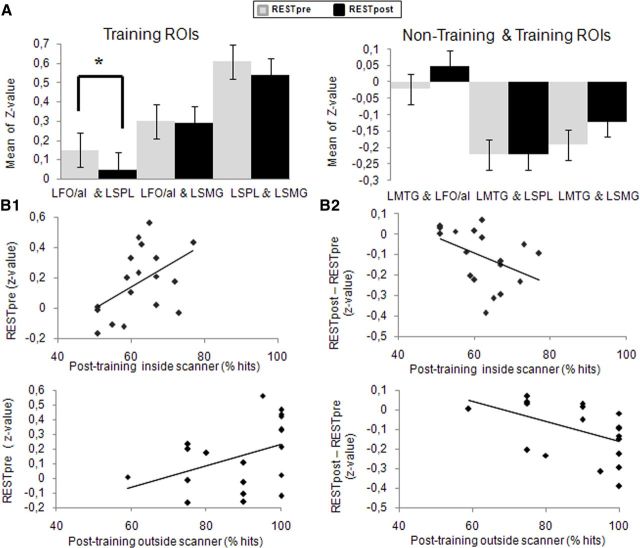
Figure 5.
Changes in rs-FC associated with nonnative phoneme identification training in Experiment 1. A, Comparison of pairwise correlation coefficients (z value) of “training ROIs” (LFO/aI, LSMG, and LSPL) and a “nontraining ROI” (LMTG) between rs-fMRI periods [light blue, pretraining (RESTpre); dark blue, posttraining (RESTpost)]. We only observed a significant decrease in rs-FC of the LFO/aI and LSPL (t(18) = 3.27, p < 0.004). B1, Pretraining rs-FC between the LFO/aI and LSPL became significantly correlated with posttraining identification performance recorded inside the scanner (rs = 0.51, p < 0.05, n = 18) and outside the scanner (rs = 0.46, p < 0.05, n = 19). B2, Changes in rs-FC between the LFO/aI and LSPL were inversely correlated with posttraining identification performance recorded inside the scanner (rs = −0.53, p < 0.05, n = 18) and outside the scanner (rs = −0.56, p < 0.05, n = 19).