Figure 3.
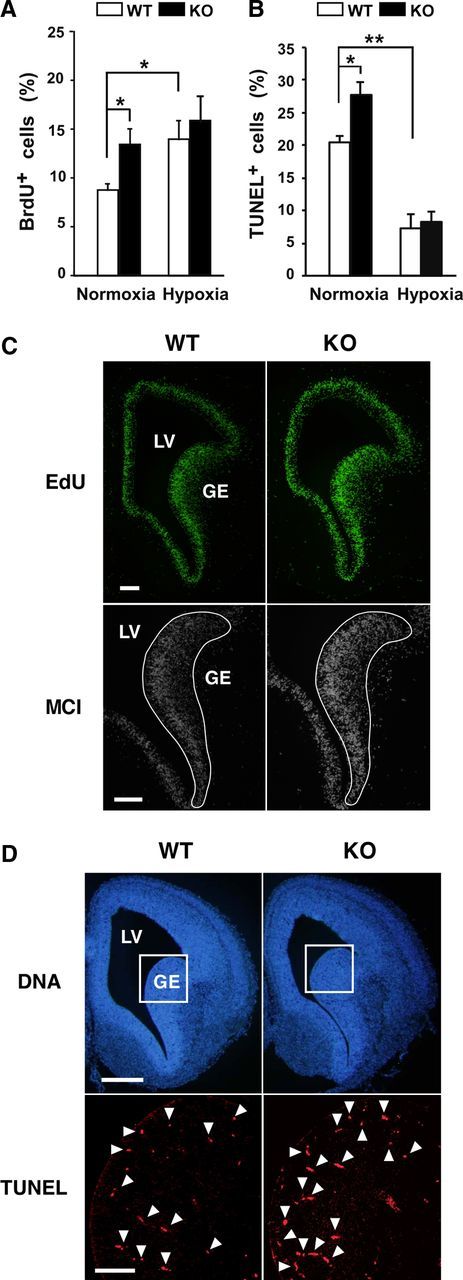
Necdin-deficient NSCs show high rates of proliferation and apoptosis. A, BrdU incorporation assay. Primary NSCs prepared from WT and KO mice were incubated in normoxia or hypoxia for 24 h, labeled with BrdU for 4 h, and stained for BrdU and chromosomal DNA. BrdU-positive cells (>150 cells analyzed; n = 3) were counted. B, Apoptosis assay. Primary NSCs were incubated in normoxia or hypoxia for 5 d, and subjected to TUNEL assay. TUNEL-positive cells (>300 cells analyzed; n = 3) were counted. A, B, mean ± SEM (n = 3). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. C, EdU incorporation assay. Pregnant mice were injected intraperitoneally with EdU at gestational day 14.5, and embryonic forebrain tissues were prepared 2 h later. Incorporated EdU in the forebrain section was observed by fluorescence microscopy. Fluorescence intensity of 12-bit digital monochrome images (MCI) inside the solid line (1.1 × 105 μm2) was quantified by fluorescence microphotometry. D, Apoptosis assay. Apoptotic cells in forebrain sections of E14.5 mouse were detected by TUNEL. Arrowheads point to representative TUNEL+ cells. TUNEL+ cells inside the square area (4.8 × 104 μm2) shown in chromosomal DNA images (DNA) were counted. Quantitative data (C, D) are in Results. LV, lateral ventricle. Scale bars: C, 100 μm; D, 200 μm (top), 50 μm (bottom).
