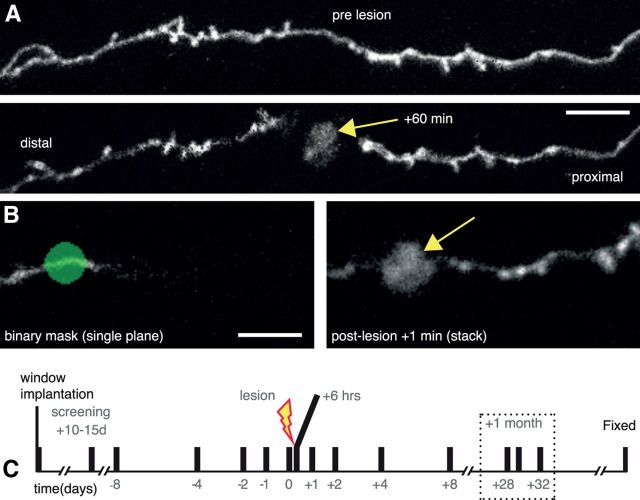
Figure 1.
Laser mediated axotomy in the living mouse brain. A, Axons undergo stereotypical retraction from the lesion site, and swelling of the axon shaft in the surviving axon (proximal to cell body). Arrow indicates the lesion site. B, A binary mask (green) at a single focal plane showing only a small part of the selected axon (left) is used to target the high-energy laser to create an axonal lesion with characteristic fluorescent mark (arrow). C, Time course for repeated imaging prelesion and postlesion to enable analysis of synaptic dynamics. Dotted box highlights the 1 month time points considered. Scale bars: A, 10 μm; B, 5 μm.