Figure 5.
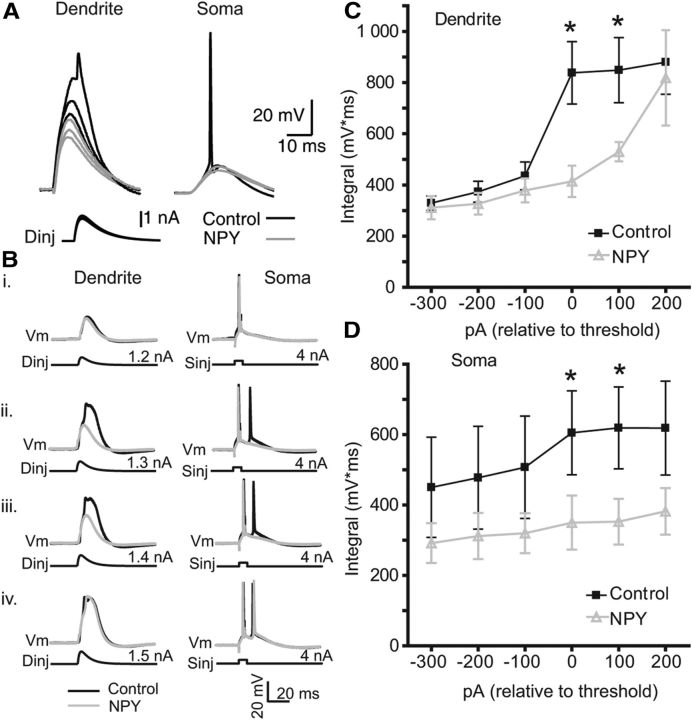
NPY inhibits the threshold for dendritic spike generation and EPSP-bAP pairing. A, Recordings were made at the distal dendrite (>500 μm from soma; left) and soma (right) of an L5 PN as in Figure 1. Current injection of increasing amplitudes (see Materials and Methods) applied at the dendrite elicited nonlinear dendritic potentials, the largest of which in turn induced action potentials at the soma (black). In the presence of NPY (2 μm), responses to the same dendritic stimulus amplitudes were substantially attenuated. Bi–Biv, Somatic APs were elicited at the soma with a square-wave current injection (Sinj; 4 nA, 1 ms) and paired (Δt = 5ms) with a subthreshold distal EPSP waveform injected at the dendritic electrode (Dinj). Subthreshold pairings (dendrite, 1.2 nA; soma, 4 nA) caused no regenerative activity in the dendrite (i). By increasing Dinj amplitude in 100 pA steps, Ca2+ spikes were observed at, and above, a pairing threshold (ii; Dinj, 1.3 nA) and resulted in an additional AP at the soma (ii–iv; black traces). Bath application of NPY (1 μm; gray) had no effect on subthreshold pairing (i), but inhibited the supralinear activity above the pairing threshold, and the additional spike at the soma (ii, iii). NPY's effect was overcome with stronger dendritic depolarization (iv). C, The dendritic ∫V*, normalized to the pairing threshold before (control, black) and after NPY application (gray; n = 4). D, The ∫V * t of the somatic responses recorded simultaneously with those in C (n = 4), also normalized to the pairing threshold before (control, black) and after NPY application (gray; n = 4). *p < 0.05 (control versus NPY, paired t test). Error bars indicate ±SEM.