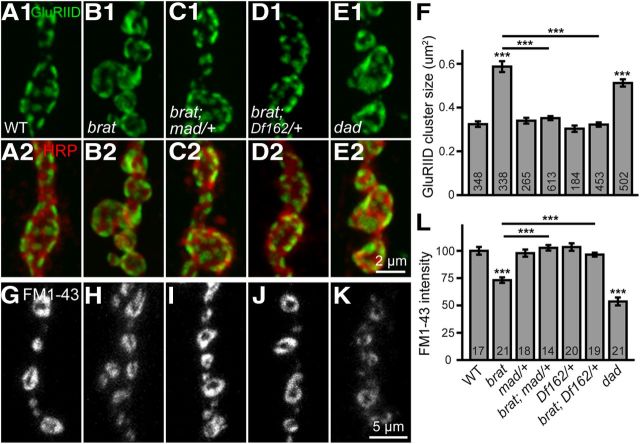
Figure 8.
Enlarged GluRIID cluster size and defective endocytosis in brat mutants are rescued by reducing the dose of mad. A–E, Confocal images of NMJ 4 boutons double-labeled with anti-GluRIID (green) and anti-HRP (red). The enlarged GluRIID cluster size in brat11/brat192 mutants (B) was fully rescued by mad12/+ (C) and Df(2L)162/+ (D) to wild-type. E, A homozygous hypomorphic dadJ1E4 also caused enlarged GluRIID cluster size. F, Quantification of GluRIID cluster size of different genotypes. The number of GluRIID cluster analyzed for each genotype is indicated in the columns. G–K, FM1-43 uptake at NMJ 4 of different genotypes. The genotypes are G, wild-type, H, brat11/brat192, I, brat11/brat192; mad12/+, J, brat11/brat192; Df(2L)162/+, and K, dadJ1E4. L, Statistical results of relative intensities of loaded FM1-43 dye at NMJ boutons of different genotypes. Scale bars: E1, 2 μm; K, 5 μm. The number of animals analyzed for each genotype is indicated in the columns. Statistical significance was calculated using one-way ANOVA (***p < 0.001; error bars denote SEM).