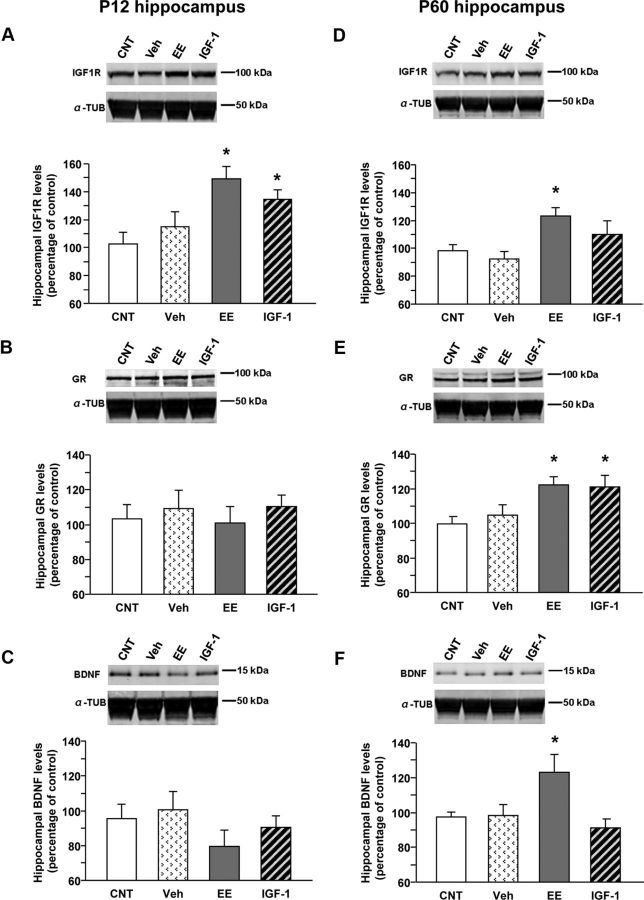
Figure 3.
Molecular mechanisms underlying EE and IGF-1 action on anxiety-like behavior: Western blot analysis of hippocampal IGF-1R, GR, and BDNF levels at P12 and P60. In all panels, the inset is a representative immunoblotting showing the corresponding protein levels in the hippocampus of animals in the different experimental groups [animals reared in standard conditions (CNT), systemically injected with saline (Veh), reared in enriched conditions up to P45 (EE), and reared in standard conditions but subcutaneously treated with IGF-1 (IGF-1)]. α-Tubulin (α-TUB) is the internal standard. A–F, Quantification of protein levels; data are mean ± SEM. Asterisks denote significant differences (p < 0.05). A, Quantification of IGF-1R levels at P12. In animals reared in EE conditions and in those treated with IGF-1, the amount of IGF-1R is significantly higher than in CNT animals, whereas saline injections have no effects (one-way ANOVA). B, Quantification of GR levels at P12. At this developmental stage, there is no difference among experimental groups (one-way ANOVA). C, Quantification of BDNF levels at P12. No difference among experimental groups is detectable (one-way ANOVA). D, Quantification of IGF-1R levels at P60. In animals reared in EE conditions, the hippocampal expression of IGF-1R is significantly higher than in CNT animals (one-way ANOVA). E, Quantification of GR levels at P60. In animals reared in EE conditions and in those treated with IGF-1, the hippocampal expression of GR is significantly higher than in CNT animals, whereas saline injections do not affect the amount of GR protein (one-way ANOVA). F, Quantification of BDNF levels at P60. In animals reared in EE conditions, the hippocampal expression of BDNF is significantly higher than in CNT animals (one-way ANOVA).