Figure 4.
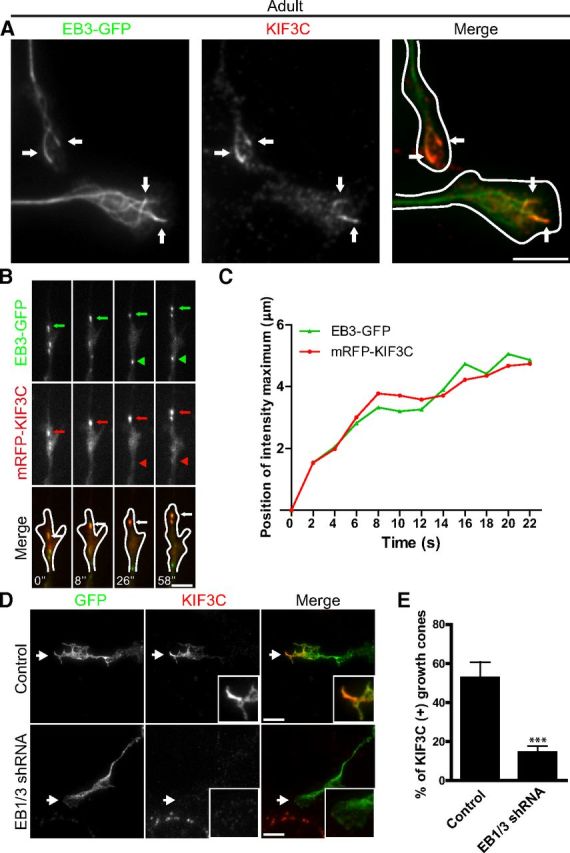
EB3 targets KIF3C to the plus-end of microtubules. A, Immunofluorescence image of an adult DRG growth cone showing that endogenous KIF3C protein accumulates at the plus-end of a subset of microtubules decorated with EB3-GFP comets (arrows). Scale bar, 5 μm. B, Simultaneous imaging of mRFP-KIF3C (red in overlay) and EB3-GFP (green in overlay) in transfected adult DRG growth cones. Selected frames from a time-lapse movie are shown; time is indicated at the bottom of the panel. A representative EB3-GFP comet (green arrows) that colocalizes with mRFP-KIF3C dots (red arrows) is indicated. An EB3-GFP comet that does not colocalize with mRFP-KIF3C is highlighted by arrowheads. Scale bar, 5 μm. C, The positions of the maximum fluorescence intensity values of EB3-GFP and mRFP-KIF3C along the moving comet track, which is indicated in Figure 3B (green and red arrows, respectively). The position of EB3-GFP in the first frame of the time-lapse was taken as a starting point. The plot shows correlated movement of EB3-GFP and mRFP-KIF3C. D, Immunofluorescence images of control and EB1/3-depleted growth cones stained for endogenous KIF3C. EB1/3 knockdown impairs the localization of KIF3C at the tip of microtubules in the growth cone (n = 282 and n = 288, respectively, compiled from three independent experiments). Scale bar, 5 μm. E, The quantification of the percentage of growth cones with microtubule tips decorated with KIF3C. Error bars indicate SD. ***p < 0.001.
