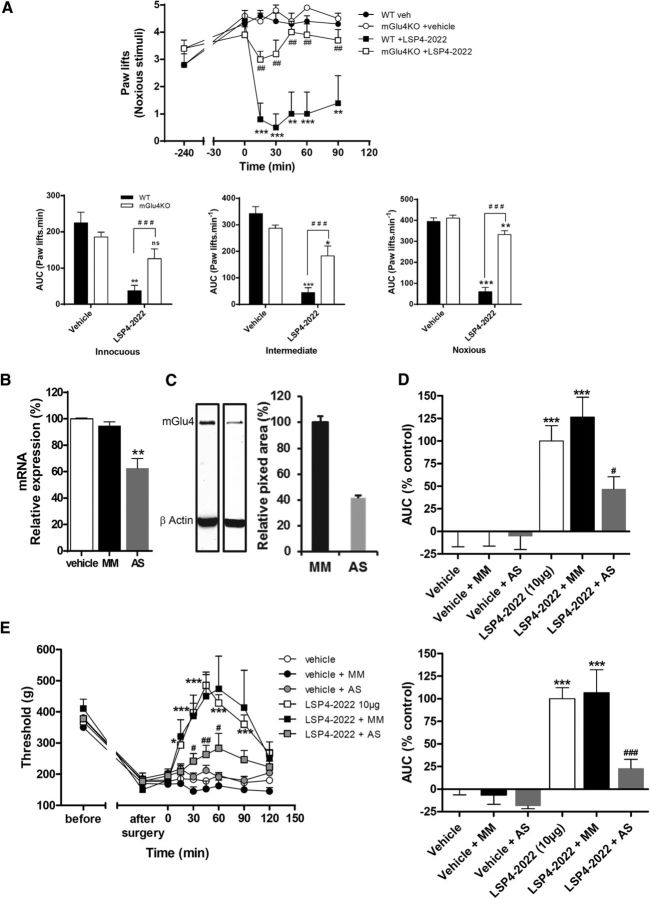
Figure 10.
Antihyperalgesia induced by pharmacological activation of spinal mGlu4 is markedly reduced in mGlu4KO mice and rats treated by selective mGlu4 AS oligonucleotides. Area under the time course curves of paw lifts after application of von Frey filaments (five stimulations) corresponding to innocuous (0.07 g), intermediate (0.6 g), and noxious (1.4 g) bending forces on inflamed mGlu4KO or WT mice treated by LSP4–2022 240 min after injection of carrageenan (A) (n = 7 animals per group). Top, Illustration of a time course of paw lifts for a noxious bending force. Bottom, Mean ± SEM of relative antihyperalgesia, expressed as the area under curve of mGlu4KO or WT mice treated by vehicle and 10 μg LSP4-2022. Quantification of selective knockdown of spinal Glu4 in rats were treated during 4 d by vehicle, scrambled control, or mGlu4 receptor targeting AS oligonucleotides by measuring DRG mGlu4 mRNA level by qRT-PCR (B) or spinal protein level by Western blot (C). Effect of mGlu4 receptor knockdown on LSP4–2022-mediated antihyperalgesia in inflamed rats (D) (n = 7 animals per group) and neuropathic rats (E) (n = 8 animals per group). Left, Time course curves of mean ± SEM of vocalization threshold to paw pressure (expressed in grams). Right, Mean ± SEM of relative antihyperalgesia, expressed as percentage of the area under the curve of rats treated by vehicle and 10 μg LSP4–2022 (control). ns, Not significant. *p < 0.05 versus vehicle-treated group. **p < 0.01 versus vehicle-treated group. ***p < 0.001 versus vehicle-treated group. #p < 0.05 versus corresponding LSP4–2022 treated WT groups. ##p < 0.01 versus corresponding LSP4–2022 treated WT groups. ###p < 0.001 versus corresponding LSP4–2022 treated WT groups.