Figure 2.
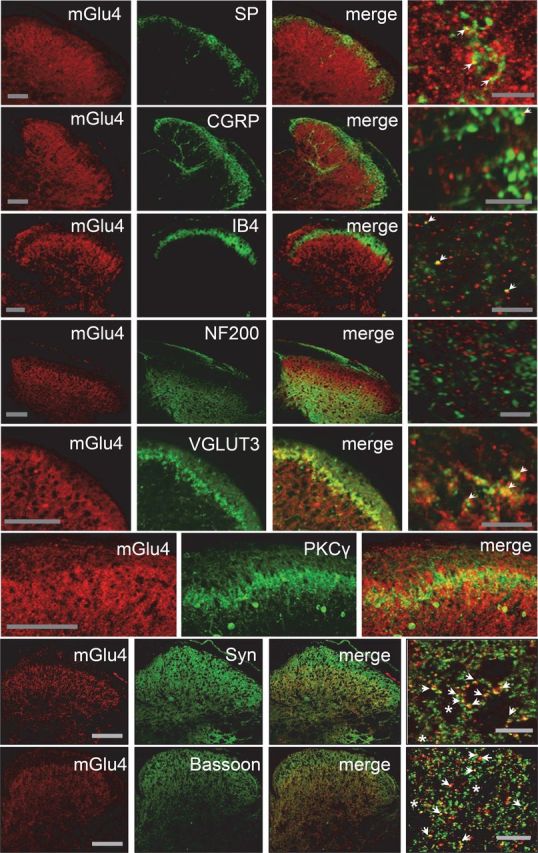
Localization of mGlu4 receptors in inner lamina II of the dorsal horn of mice spinal cord. Double immunolabeling of transverse sections of lumbar spinal cord of C57BL/6 mice with a rabbit antiserum against mGlu4 receptor (red) and various antibodies against main markers of the different sensory fibers or interneurons (green), and markers of presynaptic element (green). Immunoreactivity of mGlu4 receptors is detected in the inner lamina II of dorsal horn. The mGlu4 staining is mostly, but not exclusively, colocalized with VGLUT3 and overlaps to a large extent with interneurons that express PKCγ (green). Of note, because mGlu4 and PKCγ primary antibodies originate from the same species (rabbit), the two labeling were performed in consecutive adjacent slices. A small proportion of mGlu4 receptor staining merges with SP, CGRP, or IB4 (green) staining (arrows), whereas no mGlu4 receptor staining merges with NF200 (green). Labeling of mGlu4 and the presynaptic proteins synaptophysin and bassoon merges to a large extent (arrows), but not exclusively (asterisks). Scale bars: three left columns, 100 μm; right column corresponds to a section of the third column at higher magnification. Scale bars, 10 μm.
