Figure 4.
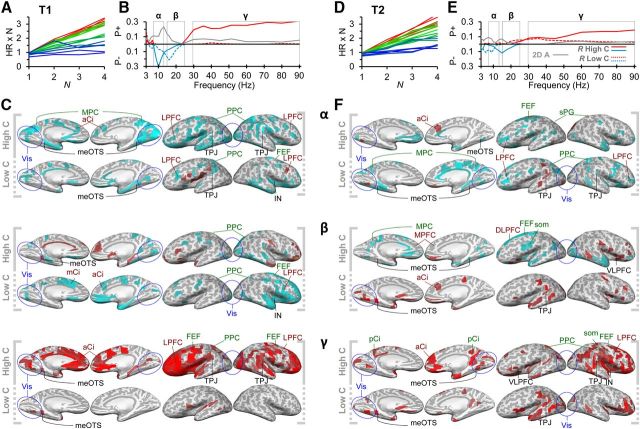
Attentional load modulates oscillation amplitudes differently in high- and low-capacity subjects. A, Individual capacity values in T1 for each subject and load condition were obtained by multiplying the target detection accuracy (HR) with the number of attended objects. The x-axis denotes the number of attended objects (N) (i.e., the attentional load). Red represents subjects with highest mean capacity in T1 and T2; blue represents those with lowest capacity. The values were used to divide the subjects into high-capacity (warmer colors) and low-capacity subjects (colder colors) (see Materials and Methods). B, In T1, attentional load strengthened γ-band amplitudes for high-capacity (solid lines) but not for low-capacity (dashed lines) subjects and suppressed the α- and β-band amplitudes differentially for high- and low-capacity subjects, respectively (Pearson's r < 0.01, FDR-corrected). These differences between groups were largely significant (gray line: two-way ANOVA, group × load interaction, p < 0.05, FDR-corrected). C, In high-capacity subjects, γ-band amplitudes were strengthened in the visual regions in OC, TC, LPFC, as well as in cingulate and orbital areas, whereas in the low-capacity subject group, these load-dependent modulations were absent. Amplitude suppression in α- and β-bands was observed in distributed areas in PPC, LPFC, and in medial cortical structures as in cingulate and insula. The color scale is as in Figure 2. D, Individual capacity values for T2 with the same subject-specific colors as in A. E, In T2, attentional load increased γ-band amplitudes both in high- and low-capacity subject groups (Pearson's r < 0.01, FDR-corrected), although the modulation was greater in the high-capacity subjects (two-way ANOVA, group × load interaction, p < 0.05, FDR-corrected) and decreased slightly α- and β-band amplitudes. F, In low-capacity subjects, α-band suppression was observed in medial cortical structures specifically in cingulate in which the amplitude suppression in high-capacity subjects was not as pronounced. In both low- and high-capacity subjects, γ-band amplitudes were load-dependently strengthened in the LPFC.