Figure 6.
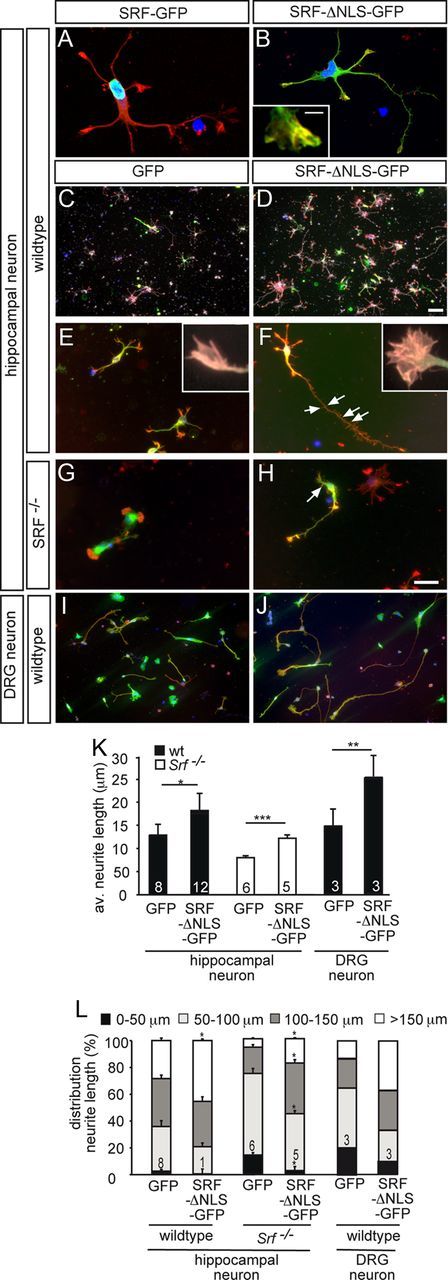
Cytoplasmic SRF stimulates neuronal motility in vitro. Hippocampal (A–H) or DRG (I, J) neurons grown for 2 d in culture were stained for GFP (green), F-actin (red), βIII tubulin (white in C, D), and DAPI (blue). A, B, A fusion protein consisting of full-length SRF and GFP (SRF-GFP) localized to the nucleus (A). SRF-ΔNLS-GFP was mainly found in the cytoplasm and also entered neurites and growth cones (B). Cytoplasmic SRF colocalized with F-actin in growth cones (see insert in B). C, D, In wild-type neurons, overexpression of SRF-ΔNLS-GFP (D), in contrast to GFP (C), resulted in increased numbers of βIII tubulin-positive neurons. E–H, SRF-ΔNLS-GFP (F, H) enhanced growth cone area, filopodia number, neurite length, and overall F-actin content in wild-type (F) and SRF-deficient (H) neurons compared with GFP (E, G). Inserts in E and F show individual growth cones. Number of secondary branches (arrows in F, H) was also increased by SRF-ΔNLS-GFP. I, J, SRF-ΔNLS-GFP (J) enhanced neurite length in DRG neurons compared with control (I). K, L, Quantification of the average neurite length (K) and distribution of neurite length ranging from 0 to >150 μm (L). Scale bars: A, B, E–J, 10 μm; C, D, 100 μm; inserts in B, E, F, 1 μm.
