Figure 5.
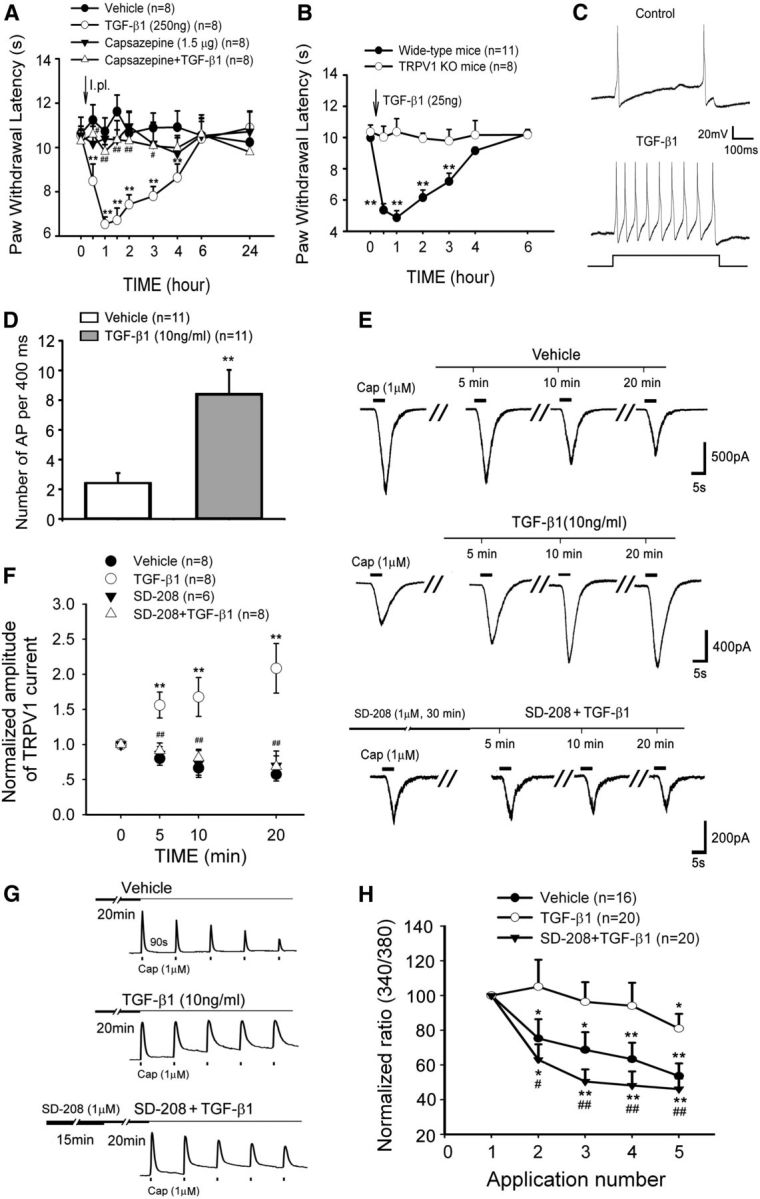
TGF-β1 evokes nociceptive behavior and potentiates action potential firing and TRPV1 function in small DRG neurons. A, An intraplantar injection of TGF-β1 acutely induced thermal hyperalgesia in naive rats. Preadministration (intraplantar) of the TRPV1 antagonist capsazepine 20 min before TGF-β1 completely prevents TGF-β1-induced thermal hyperalgesia. **p < 0.01 versus vehicle. #p < 0.05 versus TGF-β1 treatment. ##p < 0.01 versus TGF-β1 treatment. B, An intraplantar injection of TGF-β1 acutely induced thermal hyperalgesia in wide-type mice but did not in TRPV1 knock-out mice. **p < 0.01 versus wide-type. C, D, TGF-β1 robustly enhances the firing frequency of evoked action potentials obtained by a 50 pA (400 ms) current injection in DRG neurons. **p < 0.01 versus vehicle. E, Representative current traces from individual DRG neurons challenged by multiple capsaicin (Cap) applications during the 20 min treatment with vehicle, TGF-β1, or pretreatment with the TGFβRI kinase inhibitor SD-208 before TGF-β1. F, Summary data (mean ± SEM) of normalized TRPV1 currents indicate that TGF-β1 sensitizes TRPV1 currents in DRG neurons but can be blocked by pretreatment with SD-208. **p < 0.01 versus vehicle control. ##p < 0.01 versus TGF-β1 treatment. G, Representative traces of calcium imaging from individual DRG neurons challenged by five capsaicin (Cap) applications. H, Summary data (mean ± SEM) of normalized capsaicin-induced increases in [Ca2+]i reveal that TGF-β1 rescues TRPV1 desensitization through TGFβRI. *p < 0.05 versus first application of capsaicin. **p < 0.01 versus first application of capsaicin. #p < 0.05 versus TGF-β1 treatment. ##p < 0.01 versus TGF-β1 treatment.
