Figure 4.
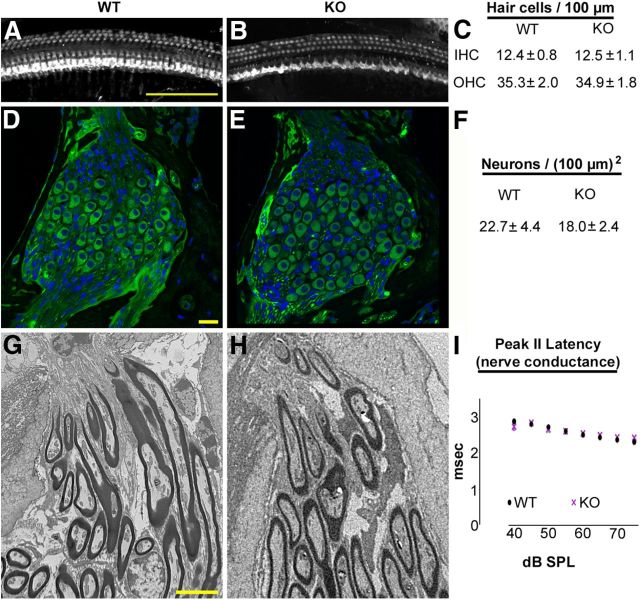
Hair cells, spiral ganglion neurons, and myelinating glial cells are present in the 4-month-old Foxo3-KO in the 32 kHz cochlear turn. A, B, Composite images of the 32 kHz cochlear turn from 4-month-old wild-type (A) or Foxo3-KO (B) mice stained with antibodies for Myo7a. Scale bar: 100 μm. C, Quantification of IHCs and OHCs per 100 μm in the 32 kHz turns from wild-type (WT, n = 3) and Foxo3-KO (KO, n = 3) whole-mount cochlear preparations. D, E, Single optical sections showing representative images of the spiral ganglion neurons in the 32 kHz turn for wild-type (D) and Foxo3-KO (E) 4-month-old mice. Anti-acetylated tubulin is shown in green and DAPI in blue. Scale bar: 20 μm. F, Quantification of neurons per unit area (100 μm squared) in Rosenthal's canal for 4-month-old wild-type and Foxo3-KO animals (n = 5 per genotype). G, H, Transmission electron micrographs of myelination of spiral ganglion neurite projections at the habenula perforata for 4-month-old wild-type (G) and Foxo3-KO (H) mice in the 32 kHz turn. Scale bar: 5 μm. I, Latency in milliseconds for peak II in the ABR traces obtained from 4-month-old animals in response to pure tones at 16 kHz, a frequency at which peak I amplitudes are affected in the Foxo3-KO mouse (Fig. 3G). Black circles: wild-type; purple X's: Foxo3-KO.