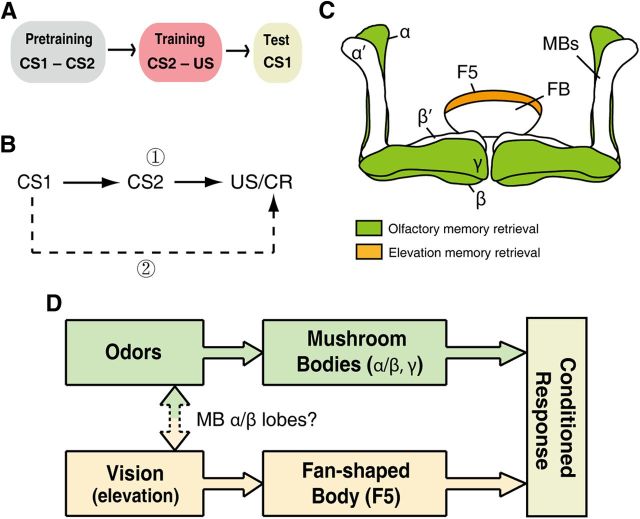
Figure 6.
A model of memory retrieval processing of cross-modal SP. A, The procedure of cross-modal SP. B, A schematic representation of hypothetical associations that could be formed for memory retrieval processing of cross-modal SP. The solid arrows indicate the pathway of the former model for CS1 memory retrieval; the dashed arrow represents another hypothetical pathway for CS1 memory retrieval. C, Anatomical representation of unimodal memory retrieval. Separated neural structures for olfactory and visual elevation memory retrieval: the α/β and γ lobes of MBs are necessary for olfactory memory retrieval; F5 is necessary for elevation memory retrieval. D, A model of a circuit for memory retrieval of cross-modal SP. Two memory traces are formed after CS2 conditioning, each of which can be retrieved independently. The two pathways could correspond through the olfaction–vision association, which may require the α/β lobes of MBs. CR, Conditioned response; FB, fan-shaped body.