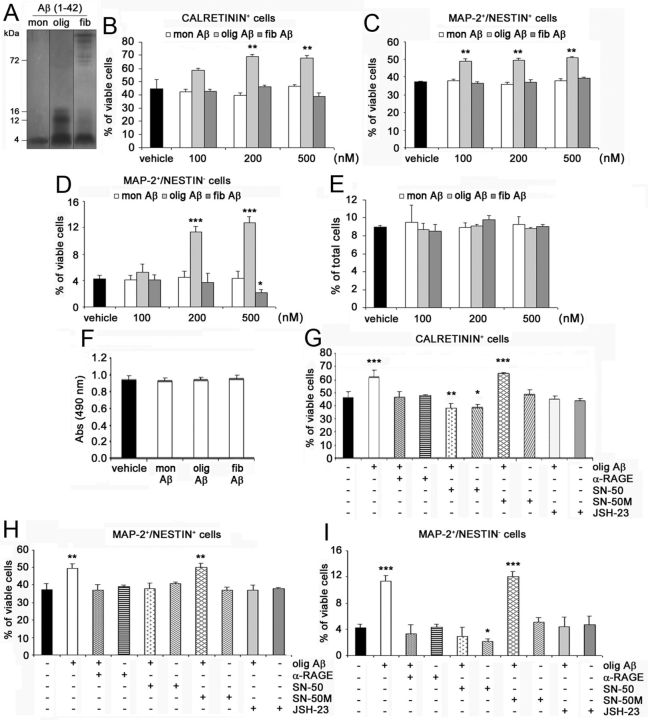
Figure 6.
Aβ1–42 oligomers promote neuronal differentiation of adult hippocampal NPCs via activation of the RAGE/NF-κB axis. A, Representative image of monomeric (mon), oligomeric (olig), and fibrillary (fib) Aβ1-42 preparations separated onto Tris–tricine gel and revealed by silver staining. B–D, One hundred to 500 nm Aβ1–42 oligomers significantly increased, compared with vehicle, the percentage of CR+ (B), MAP-2+/nestin+ (C), and MAP-2+/nestin− (D) neurons generated in WT NPC cultures. Aβ1–42 monomers and fibrils had no positive effect on neuronal differentiation of WT NPCs, with 500 nm Aβ1–42 fibrils significantly reducing the number of MAP-2+/nestin− mature neurons in cultures. E, No difference in the number of apoptotic cells in vehicle-treated and monomeric, oligomeric, and fibrillary Aβ1–42-treated WT NPC cultures. F, No difference in LDH activity released in media was observed between vehicle-treated and 200 nm monomeric, oligomeric, and fibrillary Aβ1–42-treated WT NPC cultures. G–I, In WT NPCs, the neutralizing anti-RAGE antibody (α-RAGE, 20 μg/ml), SN-50 peptide (10 μg/ml), and JSH-23 (3 μm) prevented the effect of Aβ1–42 oligomers (200 nm) on CR+ (G), MAP-2+/nestin+ (H), and MAP-2+/nestin− (I) neurons. SN-50 alone reduced the percentage of CR+ (G) and MAP-2+/nestin− (I) cells in WT NPC cultures, whereas SN-50M had no effect alone or in the presence of Aβ1–42 oligomers. B–I, Data represent the mean ± SEM of n = 3 experiments, run in triplicates. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus vehicle-treated NPC cultures (Student's t test).