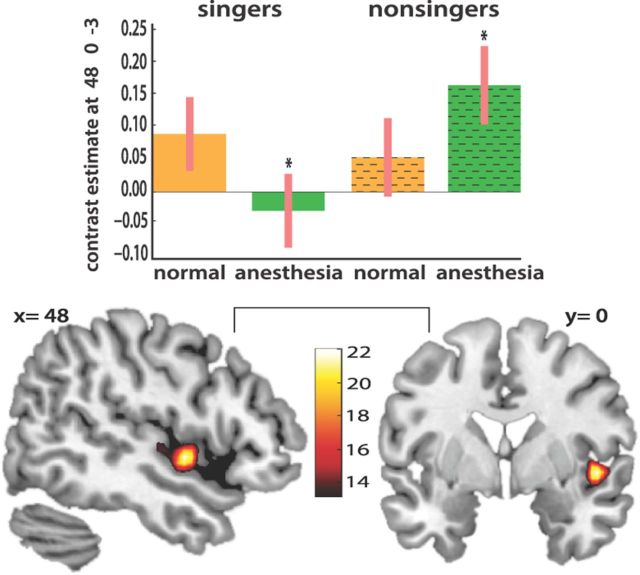
Figure 5.
Results from a linear contrast (post hoc F test) within the singing network testing the interaction between presence or absence of anesthesia across the two subject groups. The right anterior insular cortex was the principal area showing a significant dissociation across groups and conditions. For trained singers, anesthesia resulted in decreased activation of right anterior insular relative to normal singing while the opposite effect was observed in nonsingers. Bar graphs show contrast estimates and 90% confidence intervals.