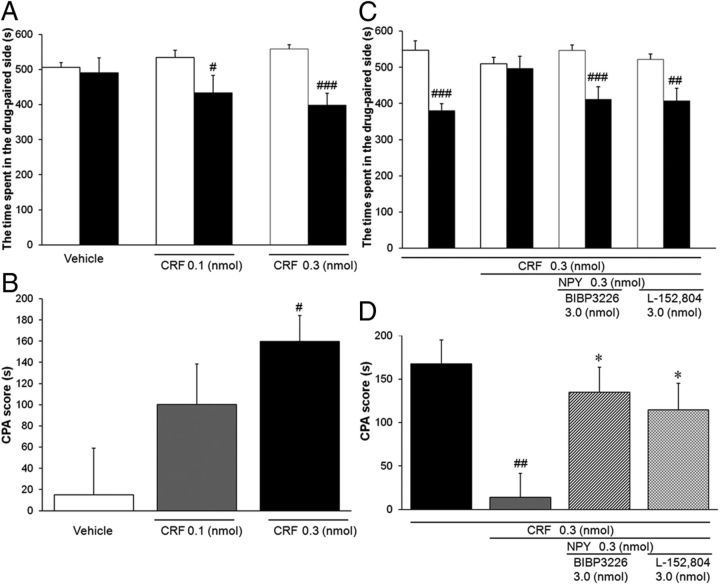
Figure 5.
Effect of intra-dlBNST injection of NPY on CRF-induced CPA. A, B, Effects of intra-dlBNST injection of vehicle (n = 10) or CRF (0.1 nmol, n = 10; 0.3 nmol, n = 11) were examined using a place conditioning paradigm. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. A, The columns show the time spent in the drug-paired compartment in the preconditioning (white columns) and test (black columns) sessions. #, ###p < 0.05, 0.001 compared with the preconditioning session (paired t test). B, The columns show CPA scores. #p < 0.05 compared with vehicle-injected rats (Newman–Keuls post hoc test). C, D, Effects of intra-dlBNST injection of NPY in the presence or absence of subtype-selective NPY antagonists on CRF-induced CPA (CRF, n = 10; CRF + NPY, n = 10; CRF + NPY + BIBP3226, n = 11; CRF +N PY + L-152,804, n = 12). C, The columns show the time spent in the drug-paired compartment in the preconditioning (white columns) and test (black columns) sessions. ##, ###p < 0.01, 0.001 compared with the preconditioning session (paired t test). D, The columns show CPA scores. ##p < 0.01 compared with CRF alone-injected rats; *p < 0.05 compared with CRF + NPY-injected rats (Newman–Keuls post hoc test).