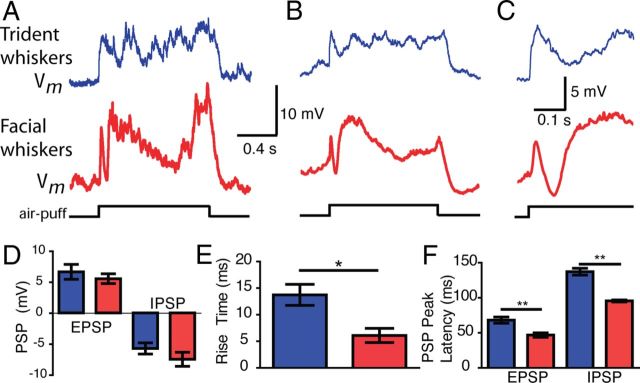
Figure 6.
Postsynaptic responses to air puffs in the trident and facial whisker representations. Whole-cell recordings from the submandibular trident (blue) and facial (red) whisker barrels. All 11 of 11 cells from the putative submandibular-trident barrel responded to submandibular-trident air puff; 5 of 5 cells from the facial whisker barrel responded to the facial air puff. A, Representative response to air puff. B, Average response from 10 trials in 1 cell. C, Initial part of the response shown in B at a higher time resolution. D, Initial EPSP amplitude and IPSP amplitude of evoked responses (p > 0.05). E, The 20–80% rise time to the initial EPSP peak in D (p = 0.014). F, Latency to PSP peak. n = 9 and n = 5 for submandibular-trident and facial whisker cells, respectively (EPSP, p = 0.006; IPSP, p < 0.0001). We corrected the absolute latencies for delays imposed by the air-puff delivery assuming an ∼8 ms response onset latency of facial barrel cortex neurons to air-puff stimulation, which we determined previously using high-speed videography (our unpublished observations). Group data in D–F indicate mean ± SE. Two submandibular-trident cells lacked an unambiguous initial EPSP phase and were not included in the group data. (t test, *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01).