Figure 5.
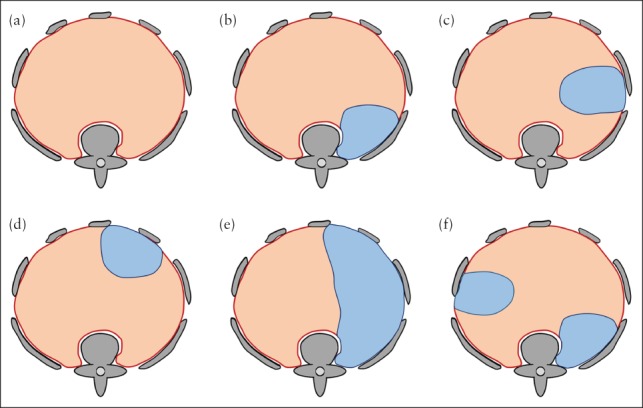
Schematic illustration of fetal MRI‐based classification system for congenital diaphragmatic hernia. (a) Normal diaphragm (red) and surrounding bony structures (gray) seen from cranially. (b–f) If diaphragmatic defect (blue) is present, it is first classified as left‐ or right‐sided, then categorized according to location as posterolateral (b), lateral (c), anterolateral (d) or hemidiaphragmatic (e). If more than one defect is present (f), each defect is classified individually; in this case, classification yields one left‐sided lateral and one right‐sided posterolateral defect.
