Figure 4.
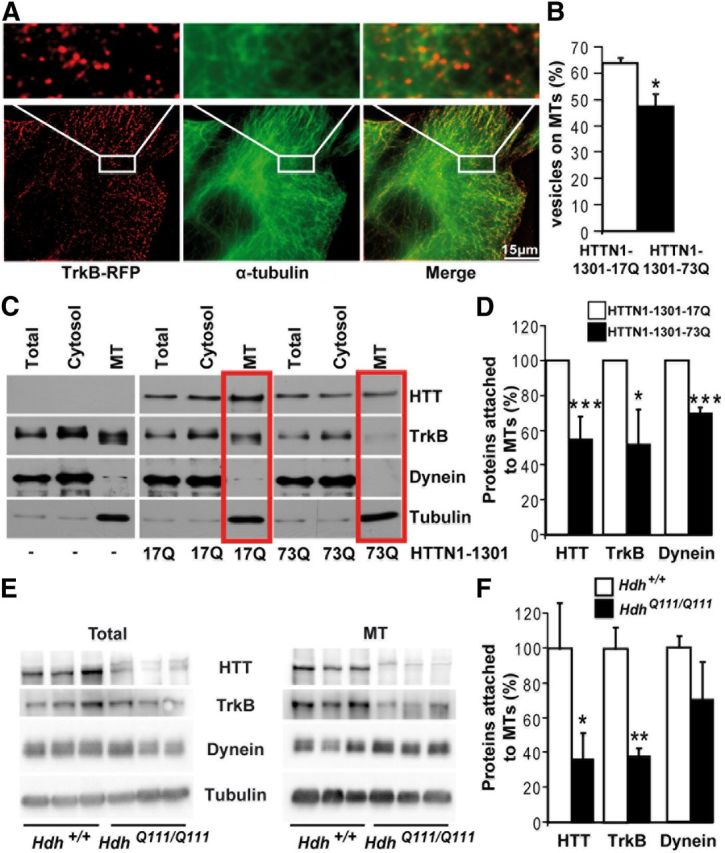
Mutant polyQ huntingtin disrupts TrkB vesicle attachment to microtubules. A, Immunostaining of Cos7 cells expressing TrkB-RFP (red) for α-tubulin (green) reveals the localization of TrkB on MTs. B, Quantification of TrkB vesicles on MTs in three independent experiments (HTTN1–1301-17Q, n = 33 cells; HTTN1–1301-73Q, n = 38 cells) shows a reduction of TrkB localization on MTs upon abnormal polyQ expansion in HTT. C, MT fractionation of cells expressing either HTTN-1301–17Q or HTTN-1301–73Q reveals a reduced association of HTT, TrkB, and dynein in pathological conditions with quantification (n = 5) in D. E, MT fractionation of Hdh+/+ and HdhQ111/Q111 mouse brain extracts shows a decreased association of TrkB and HTT to MTs in mutant situation with quantification of three independent experiments in F. Error bars indicate SEM. *p < 0.05 (unpaired, one-tailed t test). **p < 0.01 (unpaired, one-tailed t test). ***p < 0.001 (unpaired, one-tailed t test).
