Figure 1.
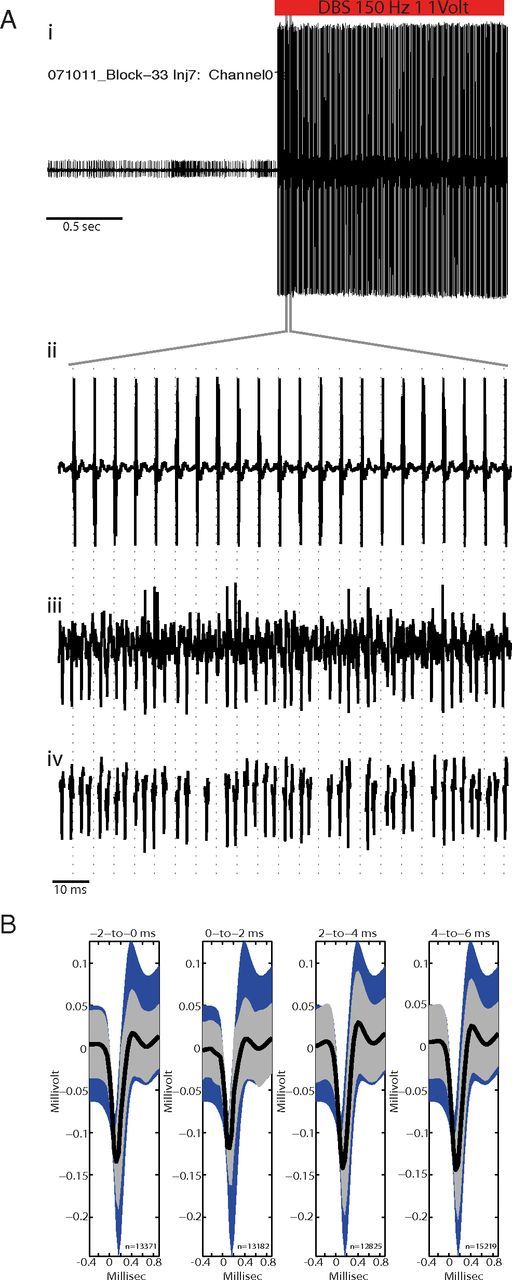
Validation of artifact subtraction method. Ai, A neuronal signal acquired just before and during GPi-HF-DBS but with artifact subtraction disabled, note the presence of large voltage transients as DBS starts. Aii, Higher magnification of the period during which DBS was activated showing the large voltage transients which occurred time locked to the delivery of the stimulation pulse (vertical dashed lines; 150 Hz, 1 V, 60 μs pulsewidth). Aiii, The same microelectrode signal acquired on a parallel acquisition channel with artifact subtraction working shows no evidence of shock artifacts while action potentials and recording noise are preserved. Action potentials that were completely obscured by artifacts in the unsubtracted data stream were easily detected in the processed data stream. Aiv, Showing action potential waveform snippets that have been processed using off-line sorting. B, Off-line test of artifact subtraction efficacy. The mean waveforms of spikes during stimulation (thick black lines; ±SEM indicated by gray shading) were required to fall within the 95% confidence interval for all spikes from nonstimulation periods (blue shading). The test was performed separately for four adjacent peristimulus intervals (indicated by time intervals above each plot). Numbers below each mean indicate the number of action potentials contributing to each mean.
