Figure 2.
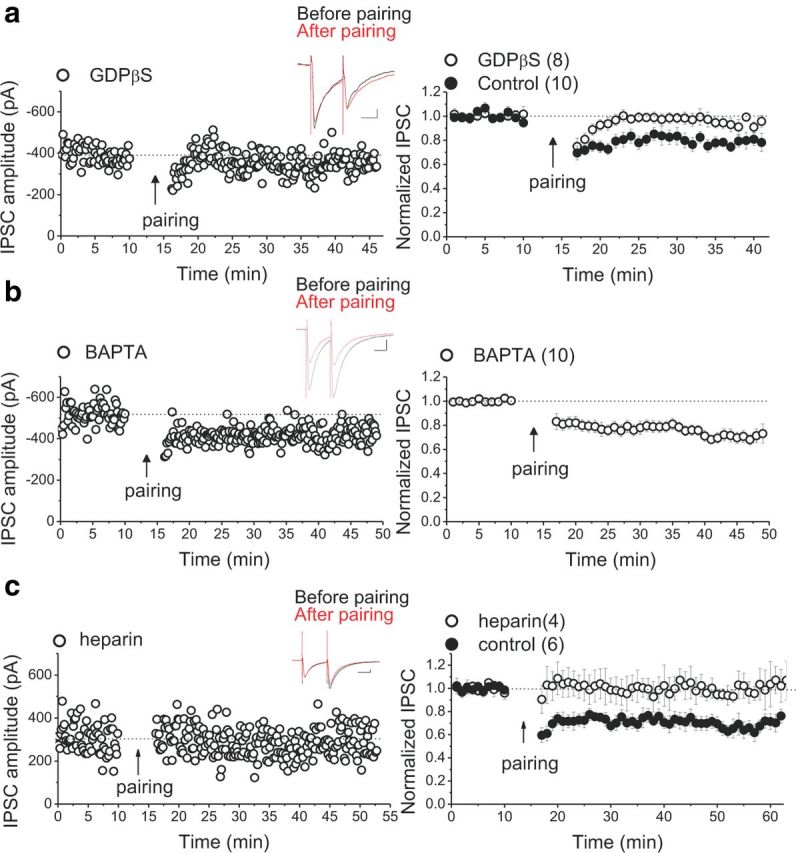
The induction of LTDGABA requires postsynaptic G-protein signaling and IP3R-mediated Ca2+ release, but chelating postsynaptic Ca2+ does not block LTDGABA. a, Single experiment illustrating the block of LTDGABA by intra-pipette GDPβS and averaged experiments with (open symbols) and without (filled symbols) 200 μm GDPβS in the pipette solution (control LTD, 78 ± 1% of pre-pairing values, F(2.28,20.55) = 8.635, p = 0.0014; GDPβS cells, 94 ± 2% of pre-pairing values, F(2.2,11.2) = 0.198, p = 0.846). Inset, Averaged IPSCs before (black) or 25 min after (red) pairing. Calibration: 50 pA, 25 ms. Disruption of postsynaptic G-protein signaling prevents LTDGABA. b, Single experiment illustrating the induction of LTDGABA with intra-pipette BAPTA and averaged experiment with 20–30 mm BAPTA in the pipette solution (open symbols, BAPTA cells, 73 ± 2% of pre-pairing values, F(3,18.39) = 18.37, p < 0.0001). Inset, Averaged IPSCs before (black) or 25 min after (red) pairing. Calibration: 50 pA, 25 ms. Intra-pipette BAPTA does not block LTDGABA. c, Single experiment illustrating the block of LTDGABA by intra-pipette heparin and averaged experiments with (open symbols) and without (filled symbols) 2 mg/ml heparin in the pipette solution (control LTD, 70 ± 0.8% of pre-pairing values, F(10.3,41.2) = 7.721, p < 0.0001; heparin cells, 1.002 ± 3.5% of pre-pairing values, F(6.17,12.35) = 0.634, p = 0.705). Inset, Averaged IPSCs before (black) or 25 min after (red) pairing. Calibration: 50 pA, 25 ms. IP3R blockade abolishes LTDGABA.
