Figure 6.
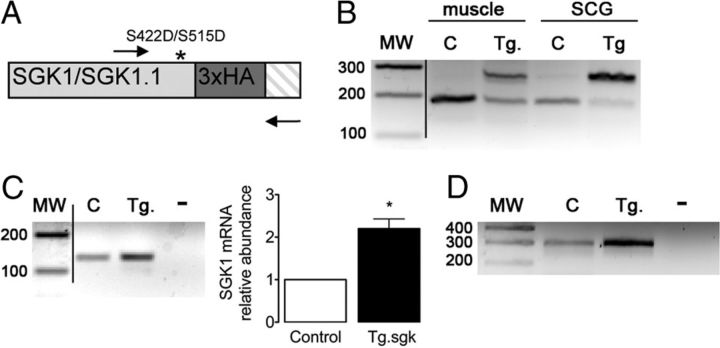
Expression of a constitutively active mutant of SGK1 in Tg mice SCGs. A, Schematic representation of the 3′ end of Tg SGK1 isoforms mRNA, which includes a triple HA tag (dark gray box) and point mutation S422D (S515D in SGK1.1) that renders the kinase constitutively active (asterisk). Arrows indicate oligonucleotides used to simultaneously study the expression of endogenous and Tg SGK1. Crosshatched box indicates the 3′ untranslated region of the transcripts. B, Agarose gel analysis of RT-PCR products obtained from skeletal muscle (tibialis anterior) or SCG from control (C) or Tg SGK1 mice using oligonucleotides flanking the 3′ end of SGK1 coding sequence, depicted in A. MW, Molecular mass markers (values in base pairs). C, Agarose gel analysis of RT-PCR products and qPCR analysis of total SGK1 transcript expression in control (C) or Tg SGK1 SCG. −, No template. Bars represent average ± SD abundance of SGK1 assessed by qPCR. *p < 0.05. D, RT-PCR products showing the expression of SGK1.1 isoform in control (C) and Tg SCG. −, No template.