Figure 3.
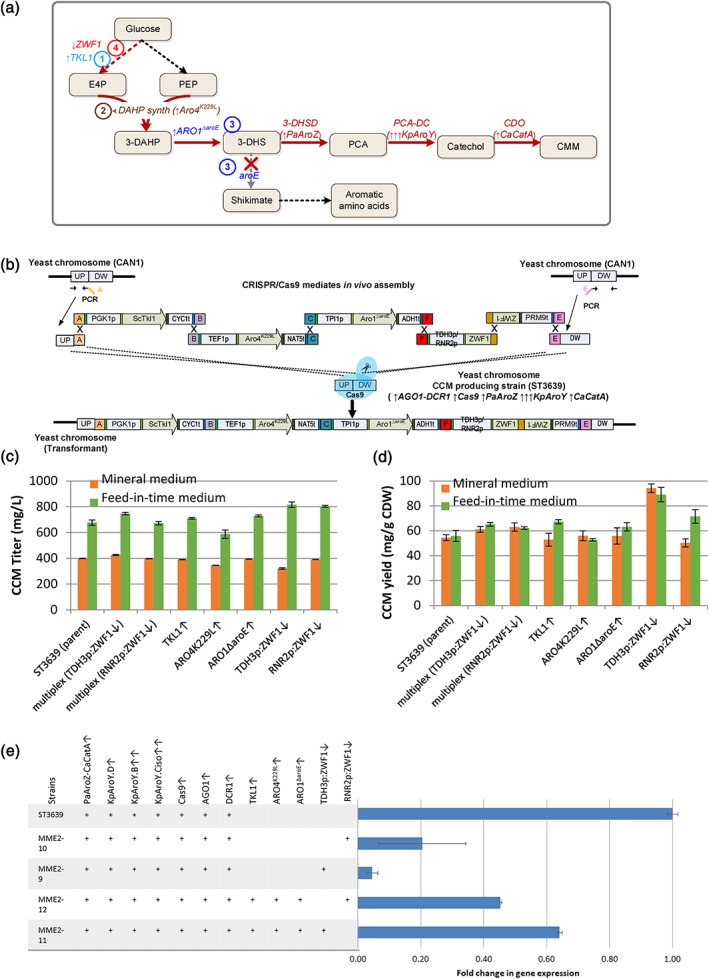
Application of CRISPR/Cas9‐RNA interference method for engineering cis,cis‐muconic acid production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. (a) Muconic biosynthesis pathway in yeast. (b) Schematic illustration of the seven‐part assembly of the three overexpression cassettes for TKL1, ARO4 K229L, ARO1 ΔaroE, one downregulation cassette of ZWF1, and homologous recombination with chromosomal target site CAN1. (c, d) Average cis,cis‐muconic acid titers and yields, respectively, in the parent strain ST3639 and engineered strains with either expression of TKL1, ARO4 K229L, ARO1 ΔaroE, downregulation of ZWF1 or multiplex expression of all combinations. Cultivations were performed in biological triplicates, and error bars represent the standard deviation of the average (n = 3). (e) qRT‐PCR analyses. Fold change in gene expression of engineered strains compared with the parent strain ST3639. ↑ indicates that a gene was expressed in a copy, ↑↑ indicates that a gene was expressed in several copies, ↓ indicates downregulation of ZWF1 under control of either TDH3p or RNR2p promoters. Error bars represent the standard deviation of duplicates [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
