Figure 1.
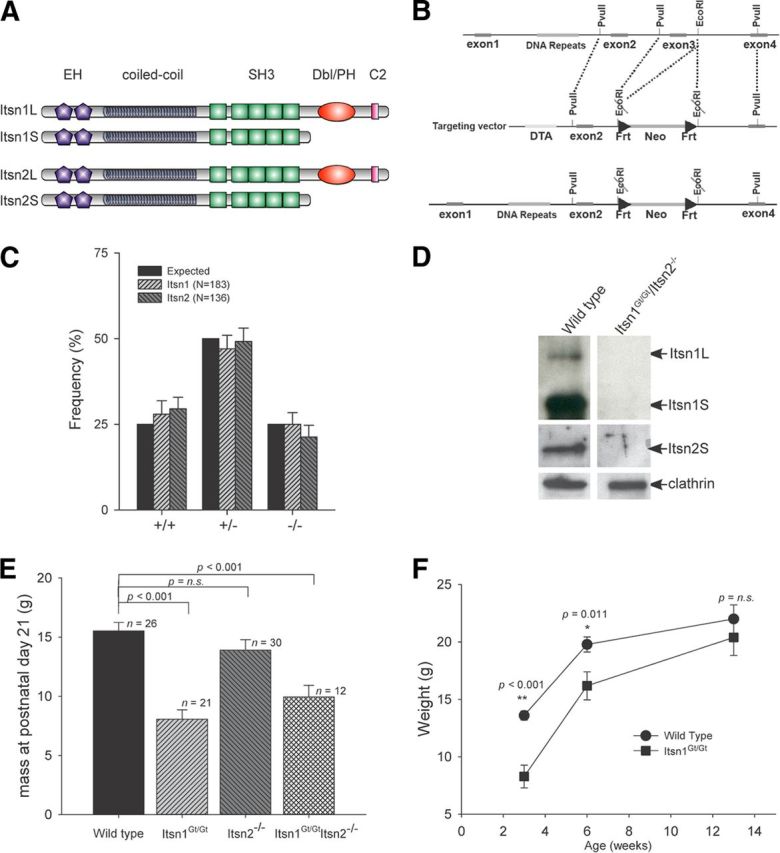
Gross phenotypic characteristics of Itsn mutations. A, Schematic representation of protein domains in major Itsn1 and Itsn2 isoforms. Each gene produces two proteins. Two EH, a coiled coil, and five SH3 domains are common to each. A Cdc42 GEF and C2 domain are specific to each long form. B, Targeting strategy for generation of Itsn2−/− mice. Exon3 was deleted resulting in a frame shift mutation. C, Offspring from breeding heterozygous mutant pairs were born at the expected Mendelian frequency. D, Western blots of whole brain lysates from double mutant mice were compared with wild-type littermates. Double mutant mice lacked expression of Itsn isoforms in the brain. E, Body mass at time of weaning (3 weeks of age). Itsn1Gt/Gt and Itsn1Gt/GtItsn2−/− mice had significantly lower body mass versus WT littermates. Itsn1Gt/Gt and Itsn1Gt/GtItsn2−/− mice were not significantly different from each other (p = 0.201). F, Itsn1Gt/Gt mice have comparable body mass to WT littermates by 13 weeks of age. p values were determined using one-way ANOVA (Holm–Sidak method).
