Figure 7.
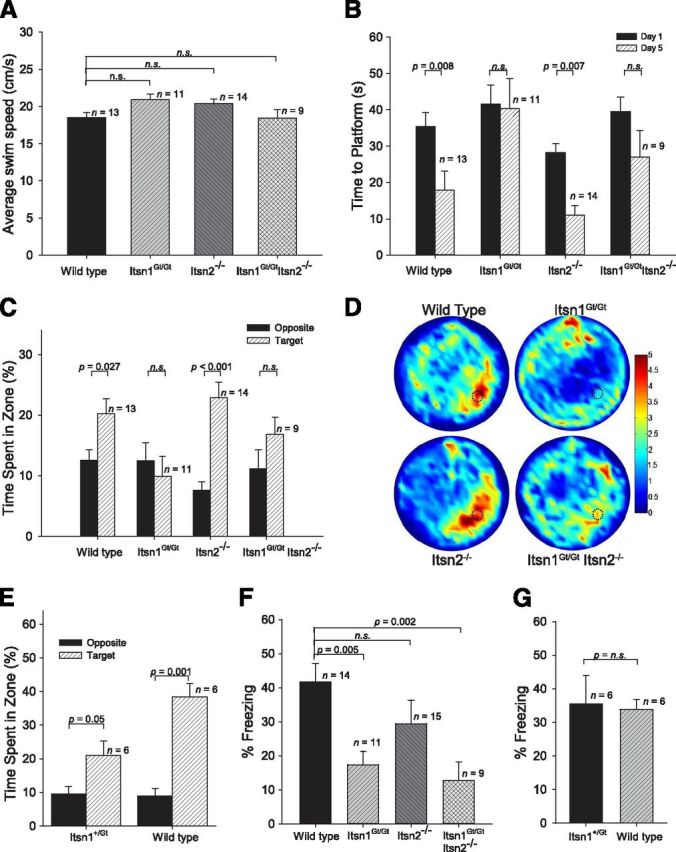
Spatial memory deficits in Itsn mutants. A, Morris water maze. Average swimming speeds of all genotypes were indistinguishable (F(3,43) = 2.79, p > 0.05). B, Summary of training days in the water maze revealed Itsn1Gt/Gt and Itsn1Gt/Gt Itsn2−/− mice did not learn the platform location after 5 d. The results of a Genotype (Itsn1Gt/Gt, Itsn1Gt/GtItsn2−/−, Itsn2−/−, WT) × Day (1–5) ANOVA shows a significant effect of Genotype (F(3,43) = 6.21, p < 0.05) and Day (F(4,172) = 15.25, p < 0.001). C, During probe tests, Itsn1Gt/Gt and Itsn1Gt/GtItsn2−/− mutants were unable to find the target platform. An ANOVA with the between-subjects variable Genotype and within-subjects variable Zone (Target, Others) revealed a significant interaction (F(3,43) = 2.77, p = 0.05) as well as significant main effects of Genotype (F(3,43) = 4.94, p < 0.05) and Zone (F(1,43) = 15.49, p < 0.001). D, Heat map summary of Morris water maze where target zone is indicated by dotted circle. Increasing color intensity (arbitrary scale) represents increased time spent. E, During Morris water-maze probe tests, Itsn1+/Gt were able to find the target platform as well as WT. F, Performance in contextual fear conditioning task. Itsn1Gt/Gt and Itsn1Gt/GtItsn2−/− mice froze significantly less than Itsn2−/− and WT mice, which did not differ. Mice with a mutation in Itsn1 showed impaired contextual fear memory (F(3,44) = 6.04, p < 0.05). G, Itsn1+/Gt mice froze to the same degree as WT mice in the contextual fear conditioning task. One-way ANOVA statistical tests were used to calculate all individual p values.
