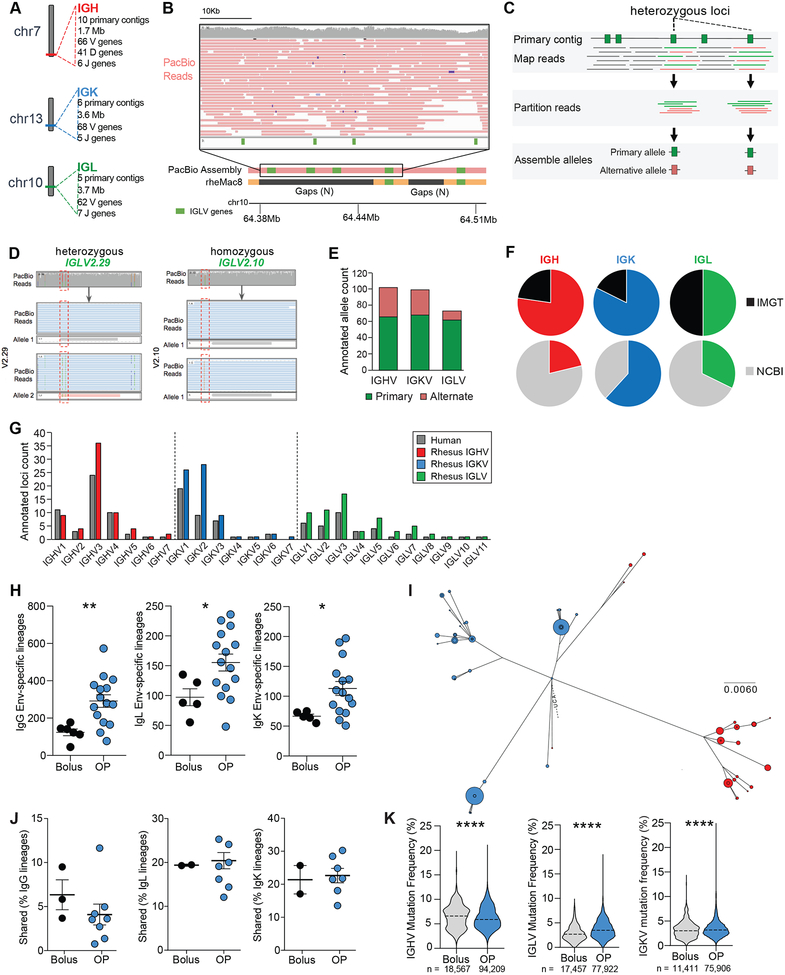
Figure 4. Immunoglobulin gene germline annotations using long-read genomic DNA sequencing.
(A) Locus and assembly summaries for the RM Ig loci.
(B) A representative region where PacBio primary contigs resolved gaps in the current RM reference genome. PacBio reads span these gaps (inset).
(C) Overview of V gene allelic variant discovery process. Reads overlapping annotations on primary contigs were assessed for the presence of SNPs, which were used to partition reads for allele-specific assemblies.
(D) SNPs (e.g., green and red) within or near genes (red boxes) were used to partition reads to each respective haplotype, allowing for the identification of heterozygous (pink) and homozygous (grey) gene segments.
(E) Primary and alternate contig alleles.
(F) Variable (V) genes from PacBio assembly that were present in IMGT or NCBI V gene repositories.
(G) V gene counts from PacBio primary contig assemblies, compared to human gene loci.
(H) Quantification of Env-specific B cells lineages from individual LNs.
(I) Phylogenetic analysis of a lineage found in both LNs in one animal. Blue, left LN; Red, right LN. Dot size represents number of reads with that sequence.
(J) Lineages shared between R and L LNs within an animal.
(K) Mutation frequencies in IGHV, IGLV, or IGKV. Violin plots; Dash = mean.
Mean ± SEM; statistical significance in H and J tested using unpaired, two-tailed Mann-Whitney U test. Significance in K tested using Student’s t-test. *p≤ 0.05, **p≤0.01, ***p≤0.001