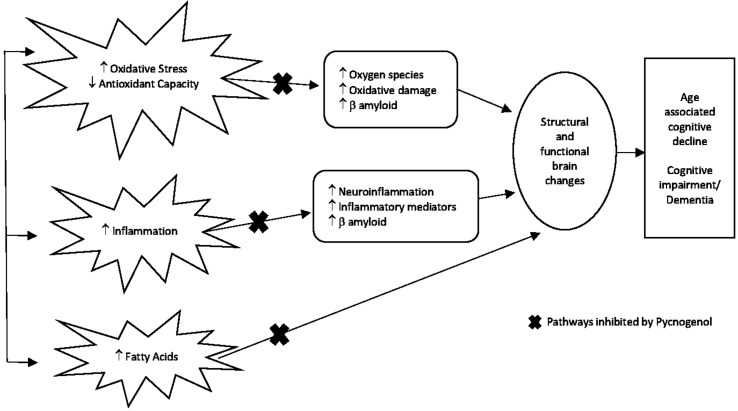
Figure 2.
Proposed mechanism of action of PYC as a targeted therapy for preventing cognitive decline. With increasing age, inflammation-reduced antioxidant metabolism leading to increased oxidative stress and damage to fatty acids are common mechanisms that over time can impact on the brain causing structural and functional changes culminating in the outcome of age-associated cognitive decline, cognitive impairment, and/or dementia. PYC potentially inhibits these mechanisms as represented by the x in the diagram due to its scavenging ability to free radicals and protection of proteins (biomolecules) against oxidative damage (Packer et al., 1999; Rohdewald, 2002; Ansari et al., 2008), neuron protection from β amyloid-induced apoptonis (Peng et al., 2002; Gulati, 2014), anti-inflammatory effects (Lau et al., 2004), and reduction of fatty acids (Sivonová et al., 2004).