Figure 1.
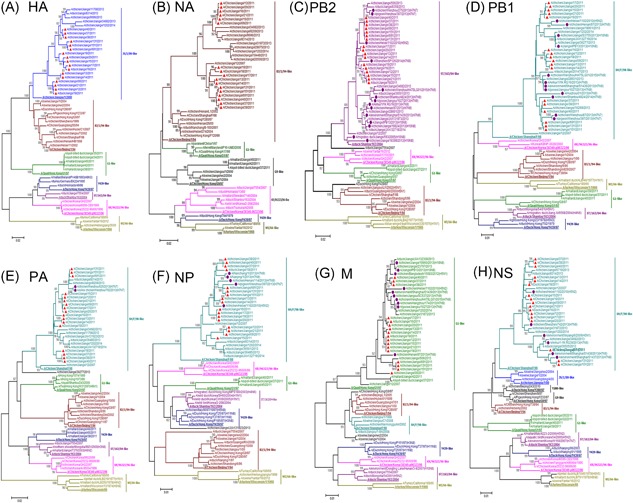
Phylogenetic trees for the HA (A) and NA (B) PB2 (C), PB1 (D), PA (E), NP (F), M (G), and NS (H) genes of all the representative influenza A viruses of the H9N2 subtype. Trees were generated by the neighbor‐joining method in the MEGA 7.1 program. Numbers above or below branches demonstrate neighbor‐joining bootstrap values. Analysis was based on nucleotides 1 to 1683 of the HA gene, 1 to 1410 of the NA gene, 1 to 2280 of the PB2 gene, 1 to 2274 of the PB1 gene, 1 to 2151 of the PA gene, 1 to 1497 of the NP gene, 1 to 982 to the M gene, and 1 to 838 of the NS gene. The sequences labeled with purple dots are HPAIVs sharing high homology with the H9N2 isolates in this study. The lengths of the horizontal lines are relative to the minimum number of nucleotide differences required to join nodes. Vertical lines are for spacing and labeling. The viruses isolated in Jiangxi were highlighted in red trigon. The names of the viruses could be found in Supporting Information Table S1. HA,hemagglutinin; HPAIV, highly pathogen avian influenza viruses; NA, neuraminidase
