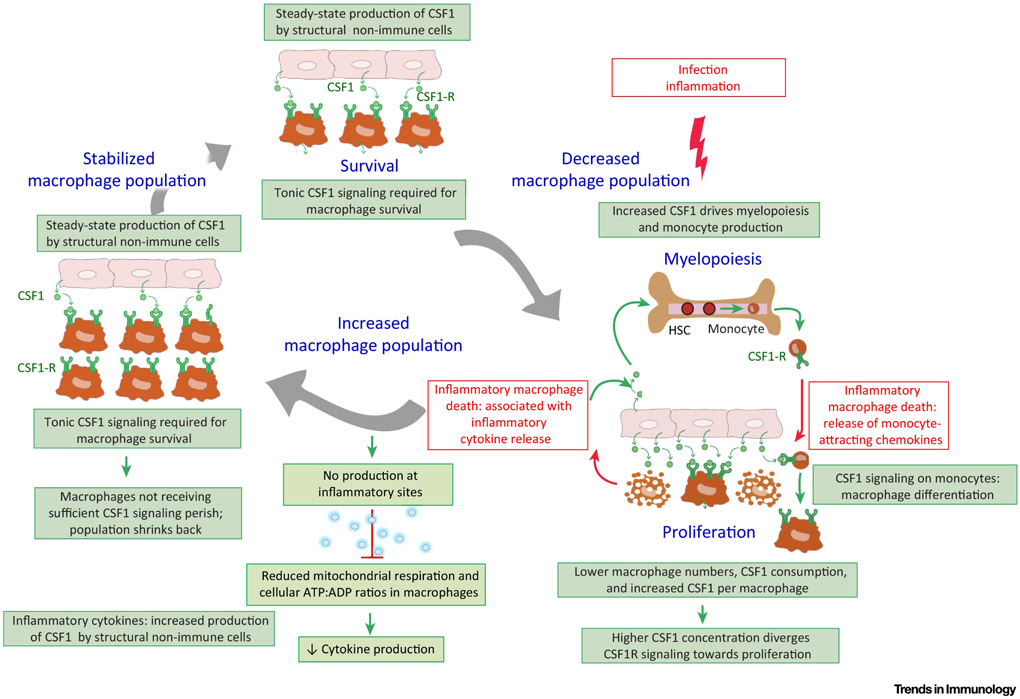
Figure 3. Quorum sensing of tissue-resident macrophages in homeostasis.
Competition for CSF1 controls the population density, as low CSF1 signaling is required for macrophage survival, while high CSF1 signaling drives macrophage proliferation. Higher concentrations of circulating CSF1 also drive myelopoiesis in the bone-marrow. Macrophage activation states can spread within the macrophage network through paracrine signaling of activating and de-activating cytokines such as TNF/IL-1β and IL-10, respectively. At inflammatory sites, nitric oxide (NO) can reduce mitochondrial respiration and cellular ATP:ADP ratios. The density of NO-producing cells can control immune cell activity at the tissue level; thus, NO production can act as a quorum sensing mechanism to help terminate inflammation.