Figure 1.
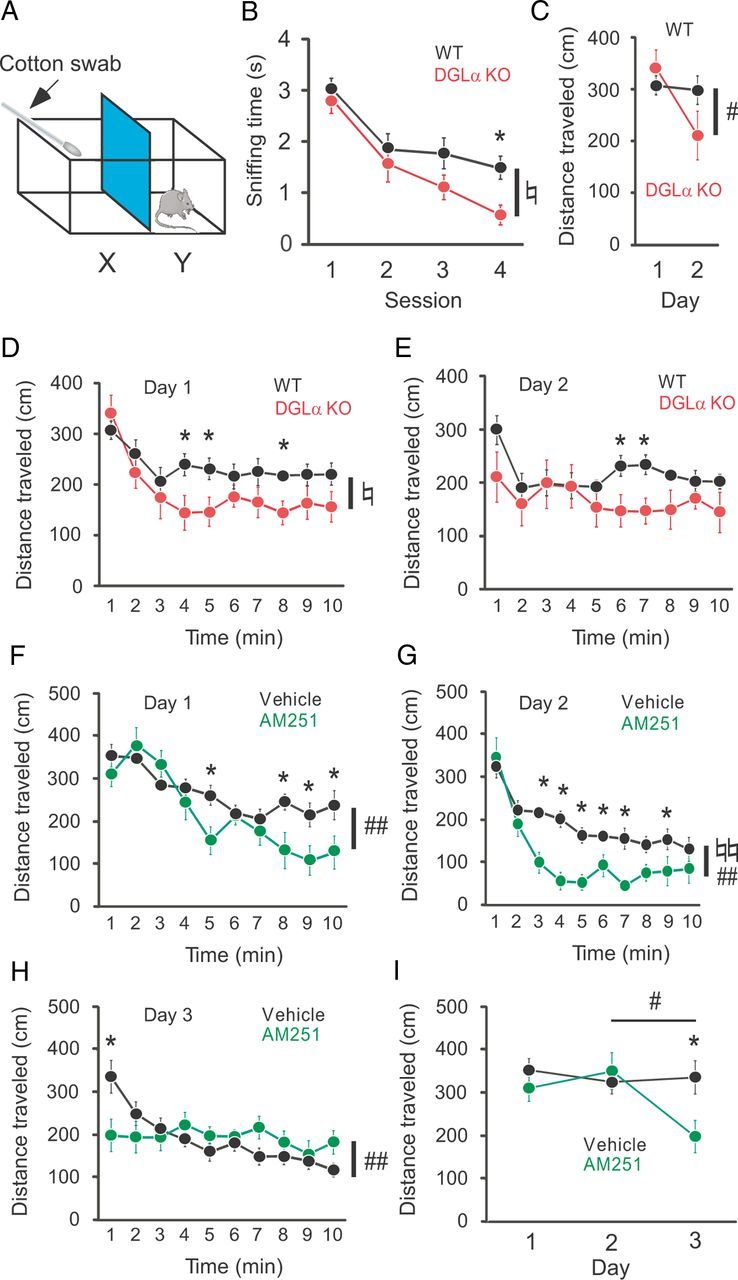
Enhanced habituation in DGLα knock-out (KO) mice and wild-type (WT) mice treated with the CB1 antagonist AM251. A, The OH chamber consisted of a Plexiglas cage separated into two compartments, X and Y, by an intervening wall. In X, a cotton swab was arranged as in the schematic. B, Changes in sniffing time during four consecutive sessions of the OH task in DGLα KO (n = 8) and WT (n = 12) mice. C, Distance traveled by DGLα KO (n = 10) and WT (n = 11) mice during the initial minute of the open-field task on the first and second day. D, E, Distance traveled by DGLα KO and WT mice during 10 min in an open field on the first day (D) and the second day (E). F–H, Distance traveled by wild-type mice treated with AM251 (n = 10) or vehicle (n = 10) during 10 min in an open field on the first day (F), the second day (G), and the third day (H). I, Distance traveled by WT mice treated with AM251 or vehicle during the first 1 min of the open field task on the first, second, and third day. Error bars indicate means ± SEM. ♮p < 0.05 and ♮♮p < 0.01 for the effect of genotype or treatment in two-way ANOVA. #p < 0.05 and ##p < 0.01 for the interaction between genotype or treatment and time in two-way ANOVA. *p < 0.05 in Tukey's test.
