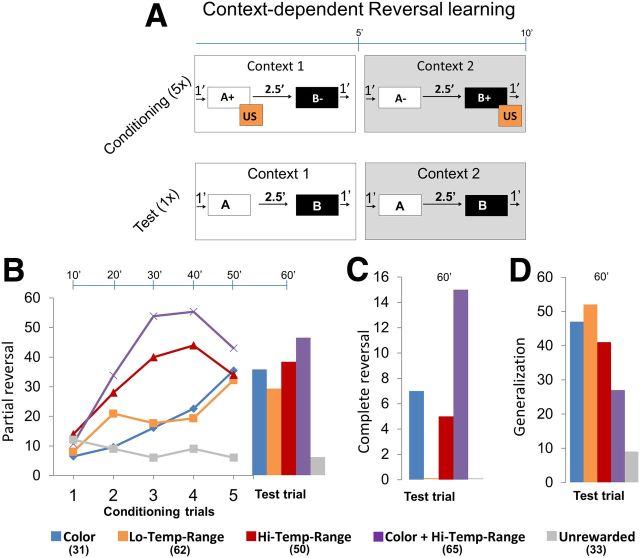
Figure 3.
Context-dependent reversal learning. A, Conditioning protocol. Each trial was 10 min long and comprised two contexts: context 1 and context 2, each for ∼5 min. Bees were randomly assigned to four groups: (1) group 1: colors (blue vs yellow); (2) group 2: low temperature range (26°C vs 32°C); (3) group 3: high temperature range (19°C vs 32°C); or (4) group 4: colors + high temperature range (yellow + 32°C vs blue + 19°C) were used as context 1 and context 2 and were balanced equally. A trial started with context 1 for 1 min and then odor A was presented for 4 s followed by sucrose reward (US) for 3 s overlapping for 1 s with A. After 2.5 min, odor B was presented but without any US. After 1 min, context 1 was turned off and immediately context 2 was presented. After 1 min, odor B was presented and paired with US. After 2.5 min, odor A was presented but without any US. Context 2 was turned off after 1 min. This comprised one trial. Bees were conditioned with five such trials followed by one test trial. In the unrewarded control experiment, the contexts and odors were presented in the same sequence but without a reward. B, Plot shows percentage bees showing partial reversal in a particular trial, for example, if a bee showed PER toward odor A in context 1 and no PER toward odor A in context 2, whereas if a bee showed no PER to odor B in either context, it is said to have learned the context rule albeit only partially (Table 2). Most of the bees showed significant partial reversal toward the rewarded context compared with the unrewarded context. Bees that were subjected to combination of two contexts color + high temperature range showed the highest partial reversal. C, Complete reversal was one in which bees showed PER toward only rewarded odors in each context. Bees subjected to combined context color + high temperature range showed the most number of complete reversals. D, Bees that showed same response to odors in each context were said to generalize. Bees from context color + high temperature range showed the least generalization. G test: group 1, G = 9.19, p < 0.01; group 2, G = 7.99, p < 0.01; group 3, G = 12.40, p < 0.01; group 4, G = 18.99, p < 0.01. Numbers in legend indicate n.