Figure 4.
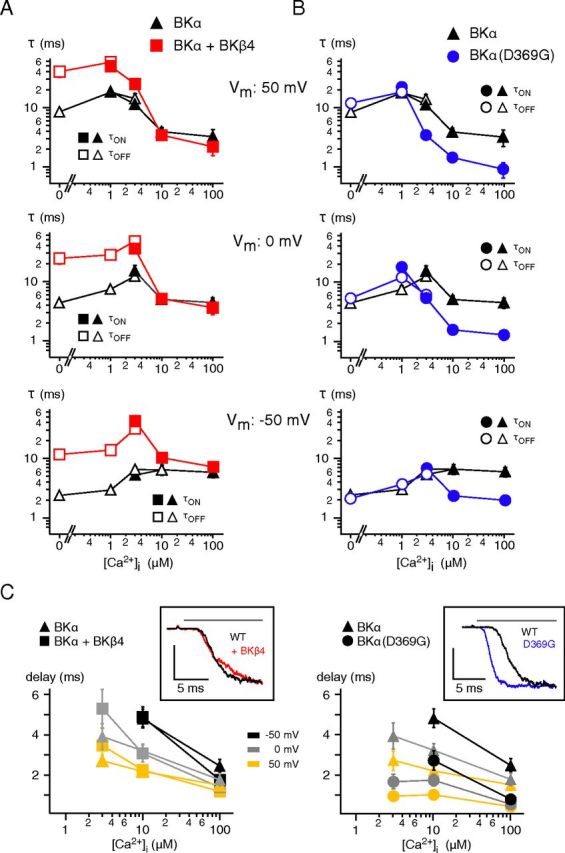
Effects of co-assembled BKβ4 and the BKα(D369G) mutation on Ca2+ gating of BKCa channels. A, B, Time constants of Ca2+ gating measured at the indicated potentials in inside-out patches from CHO cells expressing wild-type BKα either alone or together with BKβ4 (A) or expressing the BKα(D369G) mutant (B). Symbols are as in Figure 2; data points for τON are mean ± SEM 3–16 (BKα), 5–11 (BKα + BKβ4), and 6–9 (BKα(D369G)) experiments; data points for τOFF are mean ± SEM 3–16 (BKα), 6–12 (BKα + BKβ4), and 7–8 (BKα(D369G)). Note the distinct effects of BKβ4 and the D to G mutation on the gating characteristics. C, Pre-onset delay plotted versus [Ca2+]i for BKα and BKα + BKβ4 (left) and BKα and BKα(D369G) (right). Data points are mean ± SEM 7–10 (BKα), 5–9 (BKα + BKβ4), or 3–9 (BKα(D369G)) experiments. Insets, Representative current traces recorded in response to application of Ca2+ (horizontal bar) and normalized to maximum. Note the marked reduction in pre-onset delay observed with the BKα(D369G) mutant channels.
