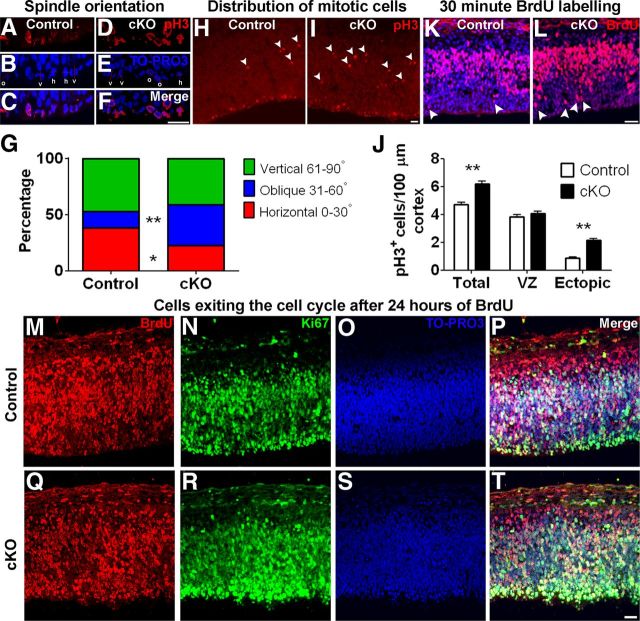
Figure 6.
Removal of MPP3 affects spindle orientation, results in ectopically localized mitotic cells, and affects migration. A–F, Determination of mitotic spindle orientation in pH3+ cells in E12.5 control (A–C) and Mpp3 cKO (D–F) cortex. G, Quantification of mitotic spindle orientation revealed that, in Mpp3 cKO cortex, there is a shift from horizontal to oblique spindle orientation. H, In E12.5 control cortex, the majority of pH3+ cells are localized in the ventricular zone at the apical membrane, with some ectopic more basally localized pH3+ cells (arrowheads). I, In contrast, in Mpp3 cKO, there are several ectopic basally localized pH3+ cells (arrowheads). J, Quantification of pH3+ cells in E12.5 cortex showed no difference in number of pH3+ cells in VZ but an increase in total number of pH3+ cells attributable to an increased number of basally localized pH3+ cells in Mpp3 cKO cortex. K, L, Distribution of BrdU+ cells in E12.5 cortex exposed to BrdU for 30 min showed no difference in total number of BrdU+ cells between control (K) and Mpp3 cKO (L) cortex but an increased number of apically localized BrdU+ cells (arrowheads). M–T, Exposure of BrdU for 24 h showed no difference in number of BrdU+ cells or a difference in percentage of cells exiting the cell cycle between control and Mpp3 cKO cortex. Cells that are BrdU+ and Ki67− have exited the cell cycle. h, Horizontal (0–30°); o, oblique (31–60°); v, vertical (61–90°); VZ, ventricular zone. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001. Scale bars, 20 μm.