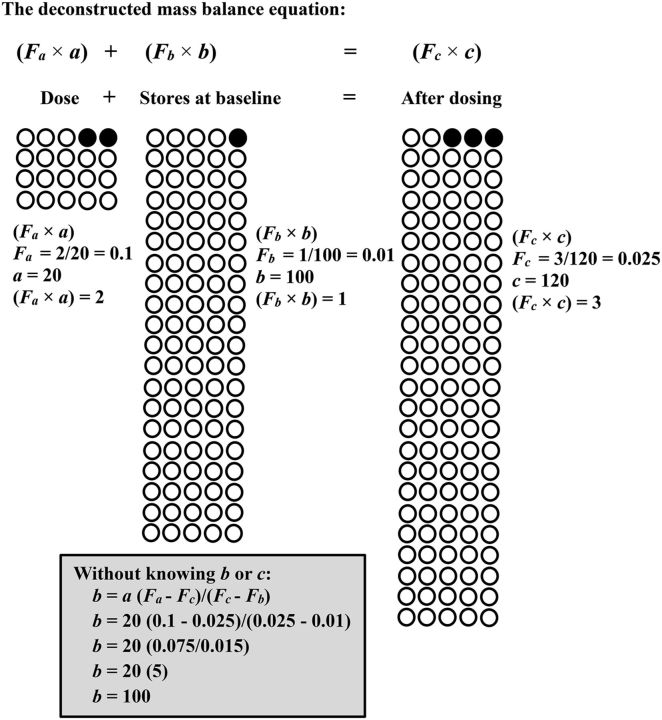
FIGURE 2.
A diagram representing the principle of stable-isotope dilution and the factors in the mass balance equation that correspond to each part of the equation using 13C-tracer as an example. Closed circles represent heavy isotopes and open circles represent light (common) isotopes. The variables a, b, and c, which refer to molar quantities in the mass balance equation, are represented in units of atoms as pictured. Fa, Fb, and Fc are calculated by dividing the number of 13C atoms by the number of total carbon atoms in a sample. An example solution of b without knowing b or c is shown: (Fa × a) + (Fb × b) = (Fc × c) is numerically verified (2 + 1 = 3) and a + b = c (20 + 100 = 120).