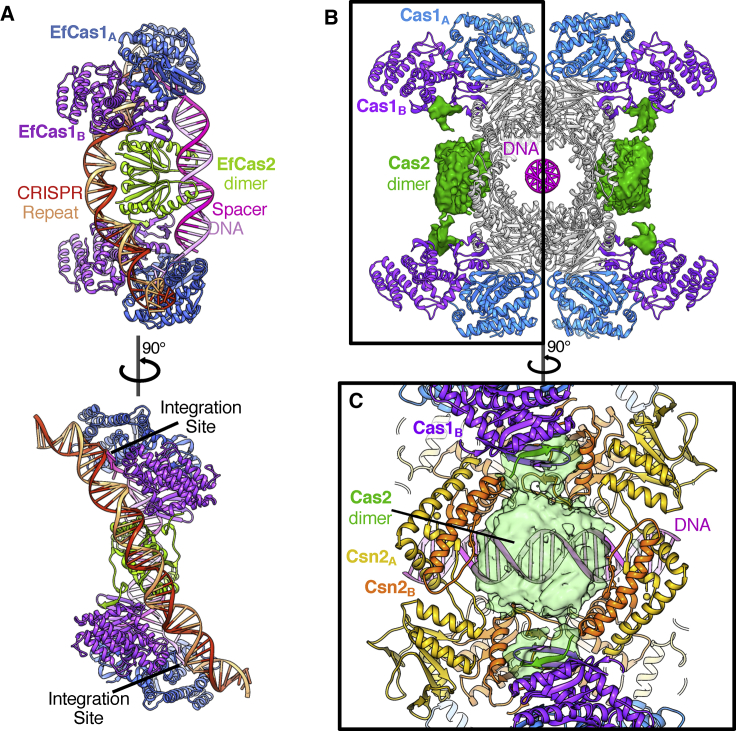
Figure 4.
Conformational Analysis of the Cas1-Cas2 Proteins
(A) The structure of the EfCas1-Cas2 integration complex (Xiao et al., 2017; PDB: 5XVP).
(B) The Cas1-Cas2-Csn2 monomer model with Csn2 (gray) highlighting the positions of Cas1 and Cas2 relative to the bound DNA. The box denotes a single Cas14-Cas22 complex equivalent to the EfCas1-Cas2 structure in (A). The density corresponding to Cas2 sits between a pair of Cas1 dimers in a similar fashion to the EfCas1-Cas2 structures. However, the bound DNA is separate from Cas2 and rotated by 90° compared to the EfCas1-Cas2 integration structure.
(C) View from the side of the monomer complex with the Cas2 density shown as a transparent surface (green). Cas2 covers a pore between Csn2 tail domains of the adjacent tetramers, thereby blocking access to the bound DNA.