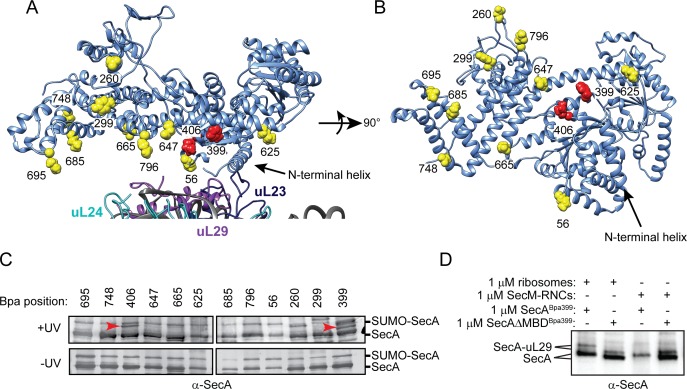
Figure 3. Site-specific crosslinking of SecA to purified ribosomes and ribosome-nascent chain complexes.
(A and B) Sites of incorporation of Bpa in the structure of E. coli SecA. (A) Fit of the high resolution structure of SecA (PDB code 2VDA [Gelis et al., 2007]) and the 70S ribosome (PDB code 4V4Q [Schuwirth et al., 2005]) to the cryoEM structure of the SecA ribosome complex (EMD-2565 [Singh et al., 2014]). (B) View of SecA from the ribosome-interaction surface. Amino acid positions where Bpa was incorporated are represented in space fill (yellow). Positions that crosslink to ribosomal proteins are coloured red. The locations of the N-terminal α-helix of SecA and of ribosomal proteins uL23 (dark blue), uL29 (purple) and uL24 (cyan) are indicated. Structural models were rendered using Chimera v. 1.12 (Pettersen et al., 2004). (C) Bpa-mediated photocrosslinking of SecA variants to vacant 70S ribosomes. 1 μM purified ribosomes were incubated with 1 μM SecA containing BpA at the indicated position and exposed to light at 365 nm (above) or incubated in the dark. Crosslinking adducts consistent with the molecular weight of a covalent crosslink to ribosomal proteins are indicated with red arrowheads. The positions of full-length SecA and uncleaved SUMO-SecA protein are indicated to the right. (D) 1 μM SecABpa399 or SecAΔMBDBpa399 was incubated with 1 μM non-translating 70S ribosomes or 1 μM arrested RNCs containing nascent SecM (SecM-RNCs) and exposed to light at 365 nm. The positions of full-length SecA and the SecA-uL29 crosslinking adduct are indicated. In (C and D), samples were resolved using SDS-PAGE and probed by western blotting using anti-SecA antiserum. LC-MS/MS analysis of the high-molecular weight bands produced by SecABpa399 and SecAΔMBDBpa399 in the presence of vacant 70S ribosomes indicated that they contained both SecA and ribosomal protein uL29.
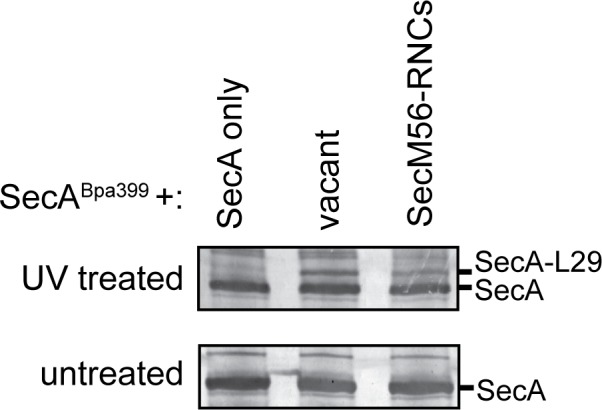
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. Crosslinking of SecABpa399 to RNCs containing arrested nascent full-length SecM and MBP.
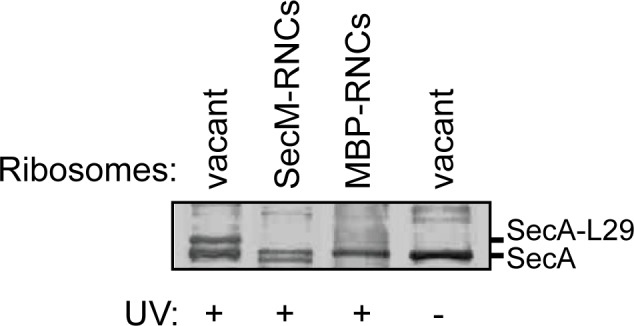
Figure 3—figure supplement 2. Crosslinking of SecABpa399 to RNCs containing arrested nascent chains with different lengths.