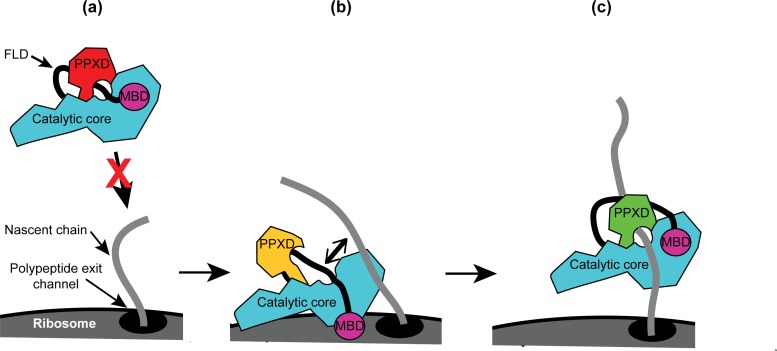
Figure 6. Diagram of the proposed mechanism for recognition of nascent substrate proteins by SecA.
(a) In solution, SecA occupies an autoinhibited conformation with the FLD bound stably in the substrate protein binding site and the PPXD in the open conformation. (b) Binding of both the catalytic core and the MBD to the ribosomal surface causes the PPXD to shift to the open conformation, which destabilises binding of the FLD and allows SecA to sample nascent polypeptides. (c) Binding to the nascent substrate protein displaces the FLD from the substrate protein binding site and the PPXD returns to the open conformation, stabilising this interaction. Binding to nascent substrate releases SecA from the ribosomal surface.