Fig. 1. Schematic of glucose-responsive charge-reversal polymers for insulin delivery.
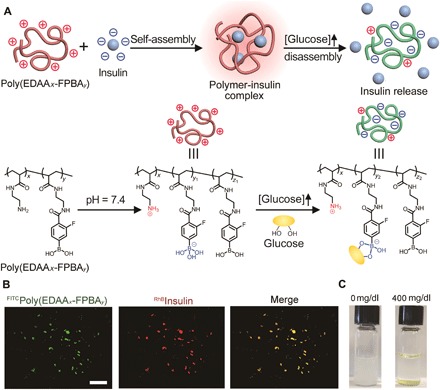
(A) Mechanism of glucose-sensitive charge reversal and enhanced insulin release from complex under a hyperglycemic state. The complex was prepared from a positively charged polymer and the negatively charged insulin via electrostatic interaction. (B) Representative fluorescence images of complex formed from poly(EDAAx-FPBAy) [green, fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)–labeled] and insulin (red, rhodamine B–labeled). Scale bar, 500 μm. (C) Representative images of the complex before (left) and after (right) treatment of glucose (400 mg/dl) for 3 hours at 37°C.
