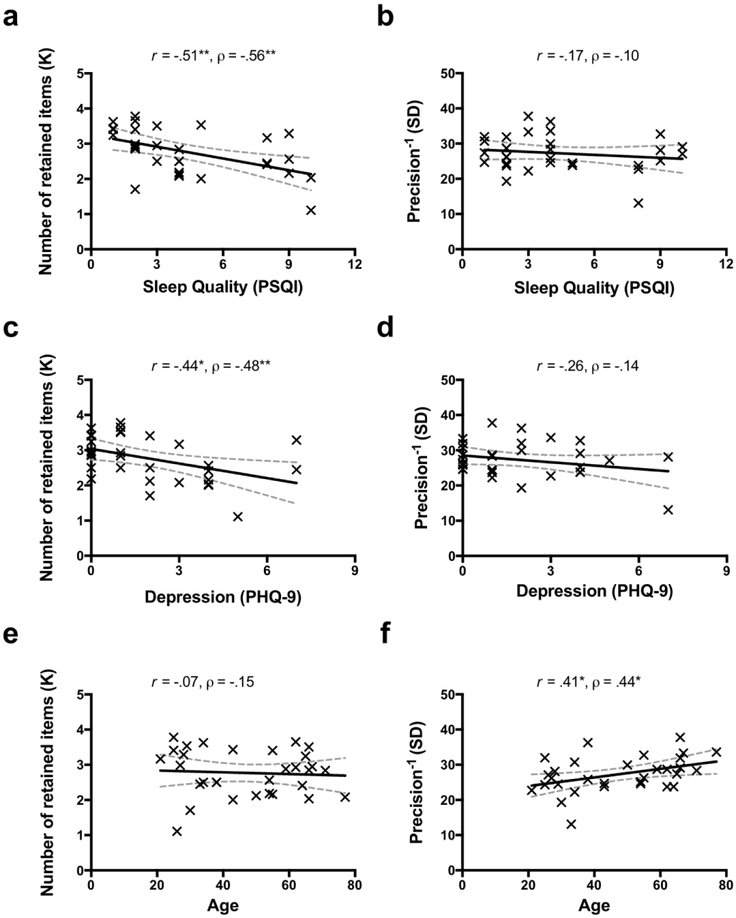
Figure 4.
The dissociable effects on working memory (WM) capacity and precision in Study 2. Sleep quality (score from the full scale of PSQI) was significantly correlated with WM capacity (a), but not with precision (b). Depressed mood (score from the full scale of PHQ-9) was significantly correlated with WM capacity (c), but not with precision (d). Age was significantly correlated with WM precision (f), but not with capacity (e). The solid lines represent the linear regression prediction. The broken lines represent 95% confidence intervals (CI) for the linear regression prediction. Pearson correlation coefficient (r) and Spearman rank-order correlation coefficient (ρ) are presented in the figure. *. p < .05, **. p < .01.