Figure 6.
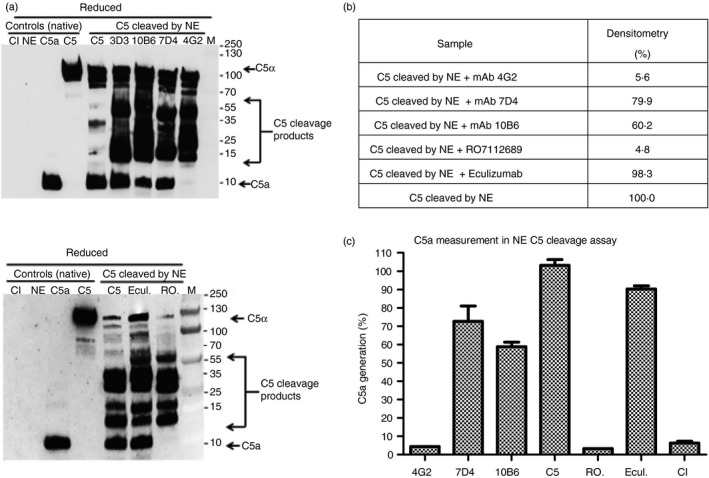
Impact of anti‐C5 monoclonal antibodies (mAb) on cleavage of C5 by neutrophil elastase. (a) Western blot of atypical cleavage of C5 by neutrophil elastase (NE). C5 was mixed with each mAb at 5× molar excess in HEPES‐buffered saline (HBS), NE was added at 420 nm, incubated and the reaction was stopped by addition of protease inhibitors. Samples (1 μg) were resolved on 4–20% SDS–PAGE gels under reducing (R) conditions and processed for WB to detect intact or cleaved C5 and C5a using an anti‐C5a mAb that also detects native C5α chain (Hycult; mAb 2942). C5α (115 000 MW), C5a (10·4 000 MW), CI; proteases cocktail inhibitors, Ecul.; Eculizumab, RO; RO7112689, 3D3; irrelevant non‐blocking anti‐C5 mAb. Note that numerous unidentified C5 cleavage products are present in all NE‐treated samples. (b) Densitometry analysis of the C5a band using imagej (expressed as % relative to the C5a generation in the absence of antibody; 100%) confirmed that mAb 4G2 and commercial mAb RO7112689 efficiently inhibited generation of C5a. (c) measurement of C5a generation by ELISA confirmed that mAb 4G2 and RO7112689 inhibited C5a generation while other mAb inhibited weakly. ELISA results are presented as percentage relative to C5a generation in the absence of any mAb (set as 100%; measured as 670 ng/ml in the ELISA). Results are representative of three independent experiments. The error bars are standard errors of triplicates.
