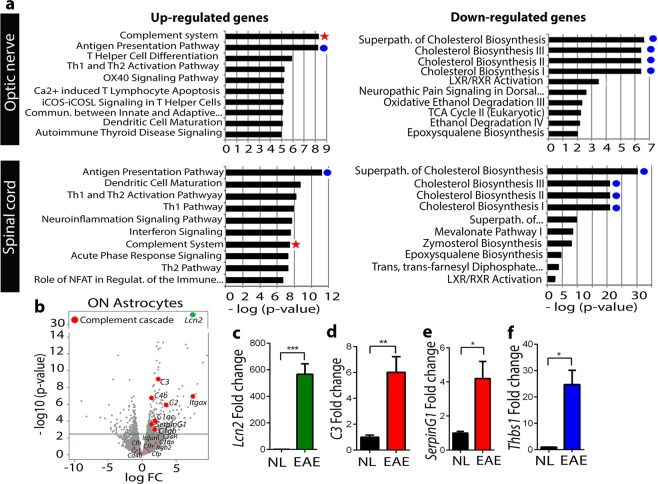
Figure 3.
High throughput sequencing and analysis of astrocyte specific RNAs identified the Complement Cascade Pathway as the most significantly uregulated pathway in astrocytes in optic nerve during EAE. (a) Pathway analysis showing top 10 most enriched and de-enriched pathways in ON and spinal cord astrocytes of EAE female mice at EAE day 50, compared to NL (n = 4 per group). The Complement Cascade Pathway (red star) was the most significantly upregulated pathway in ON, but not in spinal cord. Cholesterol bioshynthesis pathways (blue dots) were the most significantly downregulated pathways in both spinal cord and ON. (b) Volcano plot showing expression of the complement cascade genes (red dots) and the astrocyte reactivity marker Lcn2 (green dot)) in ON astrocytes at EAE day 50. Complement component C3 was the most significantly upregulated gene among the complement cascade genes, with a −log10 (p-value) of 9.27; Lcn2 (green) was the most significantly up-regulated among all genes. (c–f) Validation of RNA sequencing data by qPCR conducted on a separate set of GFAP-Cre RiboTag mice and confirming significant increase in gene expression level of the rectivity marker Lcn2 (c, green bar), complement cascade genes C3 and SerpinG1 (d and e, red bars), and Thbs1 (f, blue bar) in EAE compared to NL (black bars). Data represent mean ± s.e.m. (n = 5 per group), Student’s t-test, ***p < 0.05, ***< 0.01, ***< 0.0001.