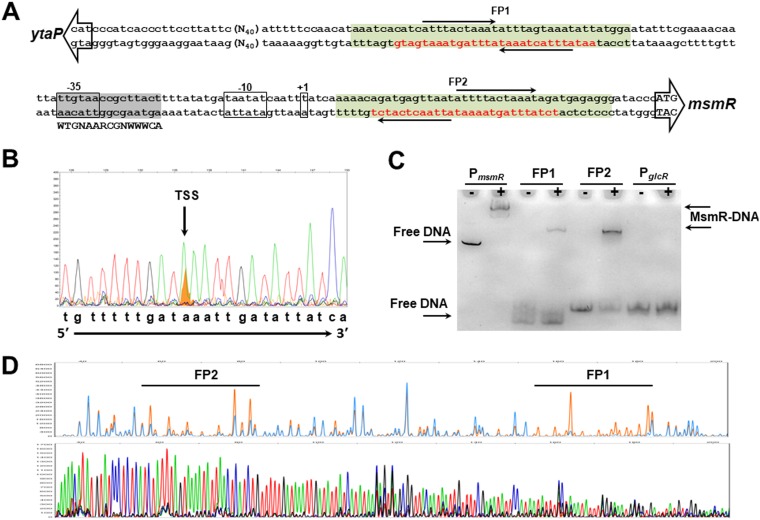
FIG 3.
Characterization of PmsmR. (A) The DNA sequence between msmR and ytaP start codons is shown. The open arrows show the start codons of ytaP and msmR. The core elements of PmsmR (−35 and −10 boxes) and the transcription start site of msmR are indicated with boxes. The protected regions of PmsmR DNA by MsmR from DNase I digestion (FP1 and FP2) are in red letters. The inverted repeats within the MsmR binding site are indicated by solid arrows. The putative cre site (gray highlighted) is also demonstrated. The green boxes show the DNA regions used for the electrophoretic mobility shift assay. (B) Identification of the transcription start site (TSS) of msmR was performed by primer extension. The migration of the generated cDNA fragment (orange) was compared with the sequencing reaction. (C) An electrophoretic mobility shift assay was carried out using 5′-end Cy5-labeled DNA fragments of PmsmR, the FP1 inverted repeat, and the FP2 inverted repeat. The amplified DNA fragment from the GlcR binding site was used as a negative control. The migration of the DNA fragment was investigated in the absence (−) or presence (+) of MsmR. (D) The chromatographs of the DNA footprinting and DNA sequencing reactions are separately shown. The 6-FAM-labeled PmsmR DNA was digested with DNase I in the absence (orange) or presence (blue) of 0.27 mM MsmR. The identified DNA footprints, FP1 and FP2, were then compared with the DNA sequencing reaction utilizing ddATP (green), ddGTP (black), ddCTP (blue), and ddTTP (red).